The new family separation: Migrant parents stranded on border send kids across alone
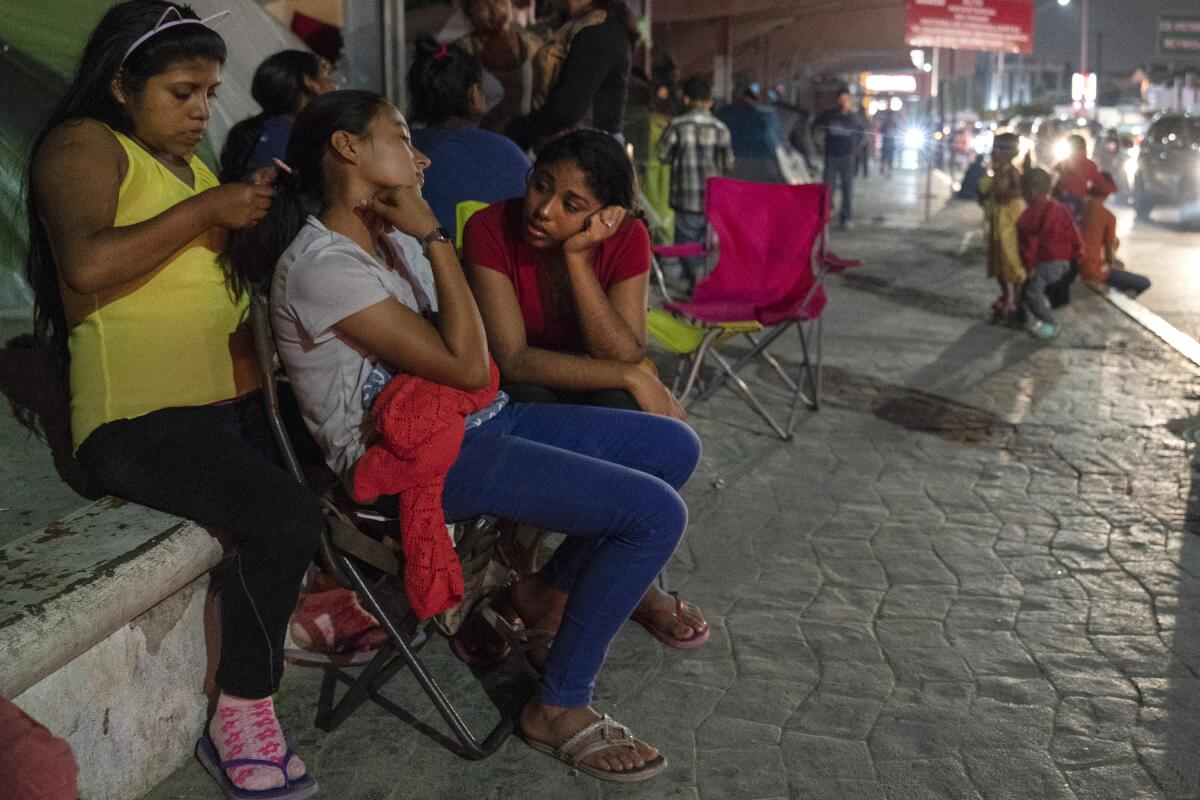
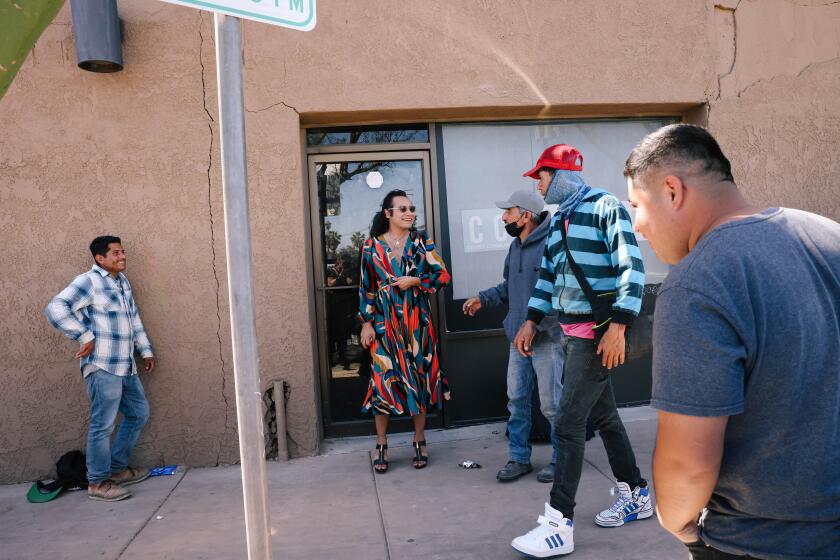
When 10-year-old Honduran asylum seeker Jose Lopez approached U.S. customs officers on the border bridge between Matamoros and Brownsville this month, they allowed him to enter Texas as an unaccompanied minor.
In fact, Jose had arrived at the border with his father Aug. 18 and requested asylum, but both of them had been sent back across the border under the Trump administration program known as Remain in Mexico. On Nov. 1, a U.S. immigration judge at a tent court near the bridge ordered them deported, his father, Delmer Lopez, said last week.
Lopez decided to give his son a chance to reach the United States on his own.
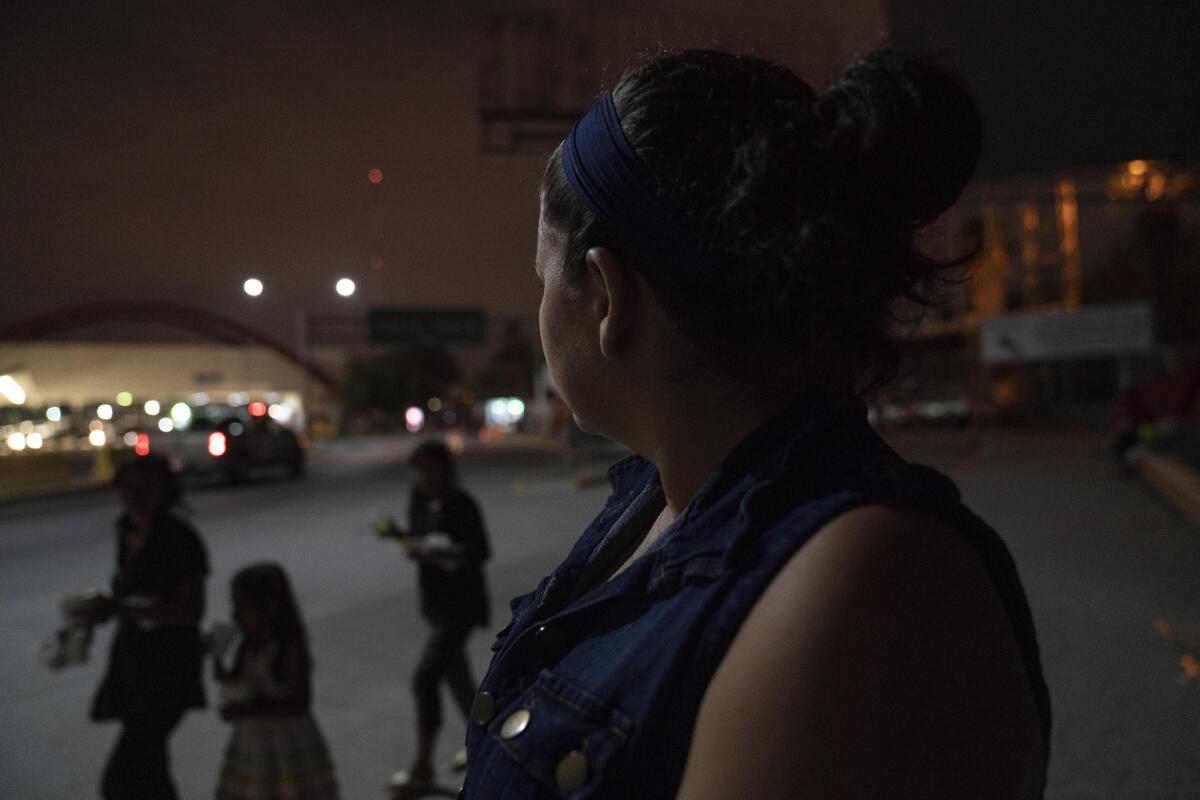
“He didn’t want to go alone,” Lopez, 36, a refrigeration technician, said as he stood near his tent in a sprawling migrant camp next to the bridge. “But as a father, I didn’t want him living like this. So I decided to take him to the bridge.”
During the last year, the Trump administration has cracked down on adult asylum seekers and families, many of them Central American. Officials stationed U.S. customs officers at the midpoints of border bridges, forcing migrants to wait to apply for asylum. They issued an asylum ban for those from countries other than Mexico and created the Remain in Mexico program, officially dubbed Migrant Protection Protocols.

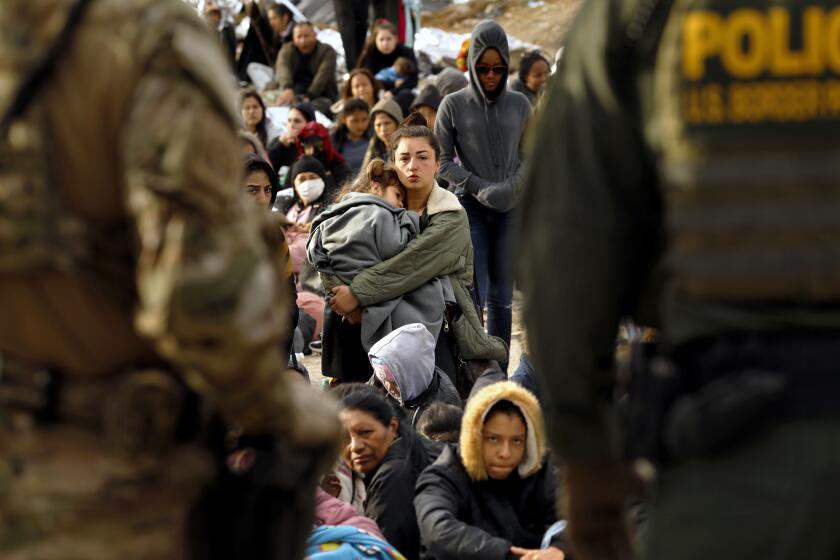
The program as of this week had required almost 54,000 migrants to stay south of the border until U.S. immigration judges rule on their asylum claims, according to U.S. Customs and Border Protection.
But children who arrive at the border unaccompanied by an adult are exempt from Remain in Mexico. By law, unaccompanied minors must be allowed into the U.S., transferred to U.S. Health and Human Services shelters within 72 hours and released to relatives or other sponsors.
In recent weeks, the exemption has led Central American asylum seekers at the largest migrant camp on the U.S. border in Matamoros to leave children on the bridge, a practice first reported by the Intercept. Critics are calling it the latest version of migrant family separation.
Health and Human Services last month started to track how many of the children who had arrived at the southern border with their families and been returned to Mexico were later referred to them by Homeland Security: at least 135, officials told congressional staffers at a briefing last week. At least 50 children from the Matamoros camp have presented themselves on the bridge as unaccompanied minors, migrant advocates estimated.

A U.S. Customs and Border Protection spokesman declined comment on the issue this week, saying only that the agency “experiences ebbs and flows with migration patterns.”
Lopez, who like most asylum seekers under Remain in Mexico doesn’t have a lawyer, appealed the deportation order issued to him and his son, but their next hearing wasn’t scheduled until Dec. 16. Conditions had deteriorated in the tent camp of more than 2,500 asylum seekers. Sometimes they didn’t eat, he said.
After hundreds of migrants last month temporarily blocked the border bridge to protest filthy conditions, Mexican child-protection workers threatened to take children into custody if families didn’t move to a new 300-bed city shelter miles from the bridge.
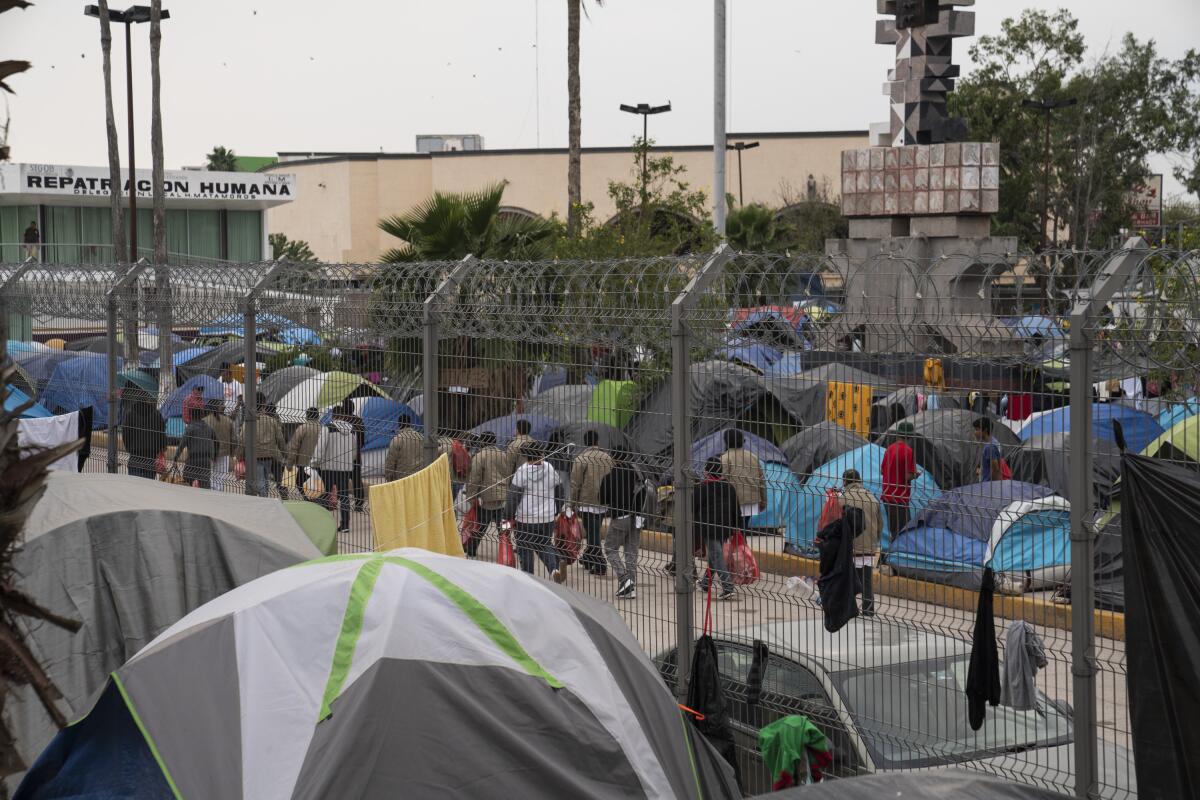

Many migrants resisted, including Lopez, preferring to stay at the bridge to more easily attend court and meet lawyers offering pro bono services. His chances of receiving asylum were slim: Through September, 9,974 Remain in Mexico cases had been completed, but only 11 migrants had received asylum, according to the Transactional Records Access Clearinghouse, a research center at Syracuse University.
Lopez thought about his wife, who had crossed the border with their now-6-year-old daughter four years ago, claimed asylum and settled in Houston. As temperatures dropped below 40 degrees, he decided his son should cross the border by himself to reunite with them.
After Jose crossed Nov. 7, he was transferred to a federal youth detention center in Houston, his father said. Lopez’s wife found Jose a lawyer at Catholic Charities, but they were not sure when he would be released.
“She said the boy called crying for me” from the shelter, he said.
Lopez knows several other parents who recently sent their children to cross the bridge alone.
“We do it because we don’t want our children to suffer,” he said. “There are lots of parents doing it.”
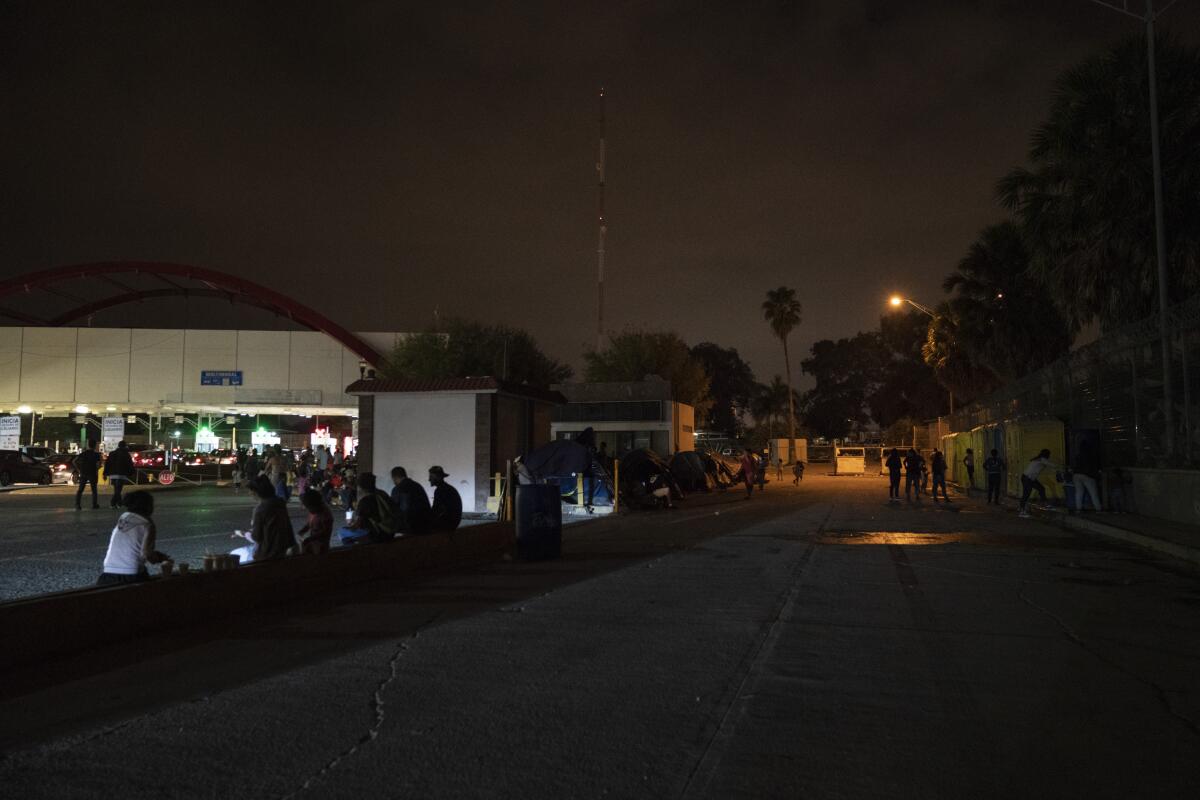
Children continued to arrive at the bridge daily without adults this week, advocates said.
“In less than an hour, I saw five kids cross,” Jodi Goodwin, a Brownsville attorney who represents migrants at the camp, said Tuesday.
As Goodwin waited for a client at the center of the bridge, she saw a teenage boy approach with a little girl clutching his belt loop and her toddler brother in his arms, sucking a pacifier. He was a 14-year-old from El Salvador; she was a 4-year-old from Nicaragua, Goodwin said.
A U.S. customs officer asked the older boy where the younger children’s parents were, and he said they had been deported, then disappeared, Goodwin said.

The customs officer asked if they had documents, Goodwin said, and the girl eagerly replied in Spanish, “I have mine! My mother gave them to me in case of an emergency.” She lifted her shirt to reveal the papers, wrapped in a plastic bag and tucked in her pants.
Goodwin said she feared her clients, a Honduran couple whose request to stay in the U.S. was refused Monday, would send their three children — ages 14, 9 and 7 — to the bridge, too.
“They should not have children out living in such a way that their parents are forced to make this kind of a choice,” she said.
At the camp last week, food, water and medicine were scarce. Parents and children bathed in the polluted Rio Grande.
Helen Perry helped set up a camp clinic last month as operations director for Global Response Management, an international nonprofit that works in war zones. The clinic sees about 60 patients a day, including dehydrated and malnourished children.
The group plans to vaccinate babies against the flu in coming days, after U.S. Customs and Border Protection decided not to vaccinate migrants before returning them to Mexico. The agency has routinely turned adults and children away from the Brownsville tent court for being sick, prolonging their immigration cases.
Perry knows two mothers who sent their small children to the bridge alone, but she and other clinic staff counsel migrants against it, worried the children could go missing.
“Until they can guarantee the safety of those kids, that’s just sending your kids to a worse fate,” she said. “We do not support the separation of parents and children under any circumstances.”
Honduran asylum seeker Jackie Cruz Rivas said she sent her 12-year-old son, Josue Cruz, to cross the bridge about three weeks ago because “he wanted to study, and you can’t study here.”
They don’t have an attorney and had been waiting at the camp for a ruling in their asylum case since August, she said. Their next U.S. immigration hearing is scheduled June 24.
Now Josue is being held at a federal shelter for migrant youths in Miami, where his mother has cousins she hopes will be allowed to claim him. Last Thursday, he called her for the first time from the shelter.
“He’s very calm there,” said Cruz, 32, a homemaker, near her empty tent at the camp last week. “At least he’s not suffering.”
Marili, 29, an asylum seeker at the camp who asked to be identified only by her first name because she had fled gang threats in Honduras, said she sent her two children — ages 5 and 3 — to the border bridge Nov. 14.
They had been waiting for a judge to rule on their asylum case since August after being kidnapped on their way to the border and held for two weeks until they paid $7,000 ransom. Their next hearing is scheduled March 5.
Marili said she hoped her children could join their father, an asylum seeker in Lodi, Calif., whom she called to alert before they crossed the bridge. She worried about their health and safety at the camp, where her 3-year-old daughter, Madeline, had already lost weight.
“Anything can happen here. You see how we live,” Marili, a former supermarket cashier, said as she sobbed beside her tent.
“It was the hardest decision I had to make in my life. But it’s the position the U.S. government has put us in,” she said.
Marili left the children at the bridge entrance with a 14-year-old Honduran boy from the camp to lead them to U.S. customs officers. She gave her 5-year-old son, Josue, a blue backpack containing their birth certificates and their father’s contact information in the U.S.
Josue resisted.
“I’ll be a good boy,” she recalled him saying, through tears. “He thought it was a punishment.”
She promised her son that his father was waiting for him in the U.S. with food and toys, she said, but he didn’t believe her.
After they crossed the bridge, the children were sent to a shelter in Houston, where Josue was allowed to call his father, Marili said. He asked why she had not claimed them.
“He’s just 5. Think what he must think of me,” she said.
Some youths at the camp have crossed on their own, without their parents’ permission, especially 17-year-olds about to lose the option to cross as minors once they turn 18.
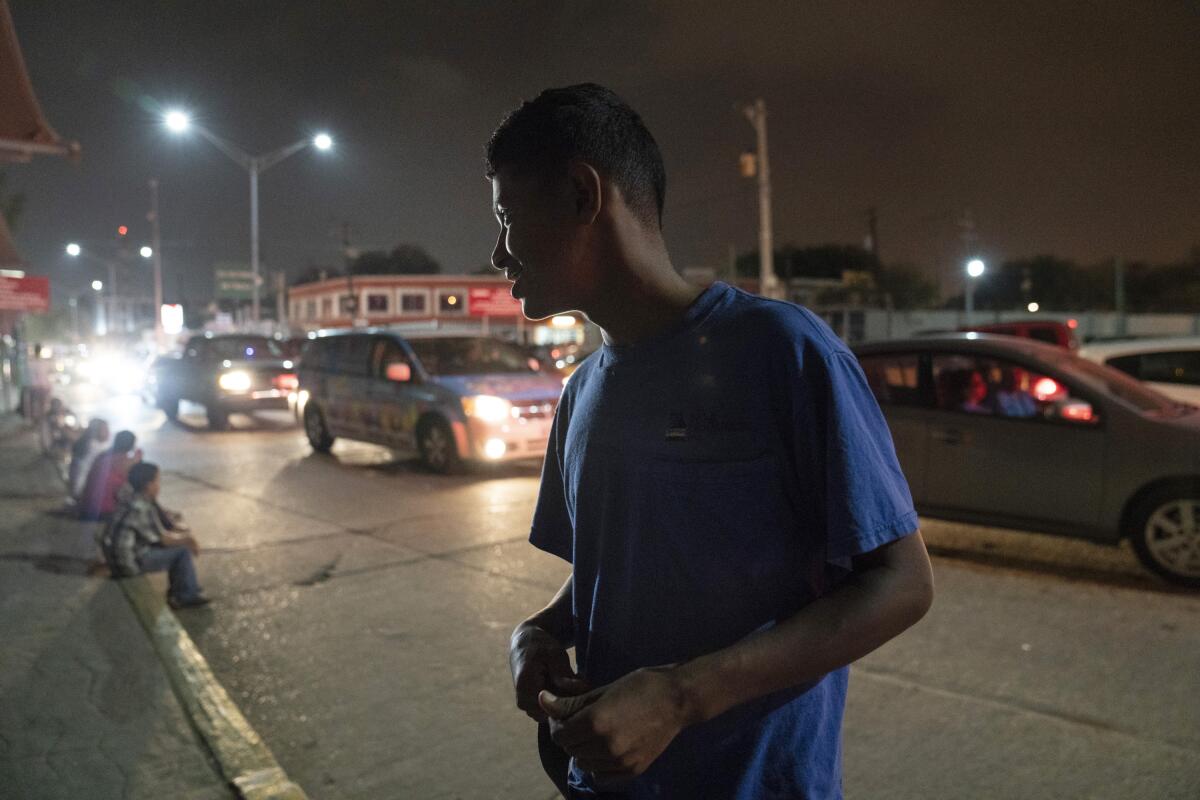
Honduran asylum seeker Denis Hernandez, 17, said last week that he was planning to cross “as soon as I have the opportunity” even though his mother wants him to stay with her.
“He can’t go without my permission,” said Marielena Quintero, 37, but that hasn’t been the case.
They arrived at the border Aug. 1, were sent back under Remain in Mexico, and their next U.S. immigration court date, their third, is scheduled Jan. 24.
Denis worried that the judge at their third hearing would order them deported, as others at the camp had been. Some of his friends had left the camp to join relatives in the U.S. and stayed in touch on social media.
He hopes to claim asylum on his own at the border bridge and join his uncle, a U.S. citizen in Virginia, but said, “It’s hard to go without my mother, not knowing what happens to her.”
More to Read
Start your day right
Sign up for Essential California for news, features and recommendations from the L.A. Times and beyond in your inbox six days a week.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.







