Federal Reserve chief says he doesn’t favor raising or cutting interest rates
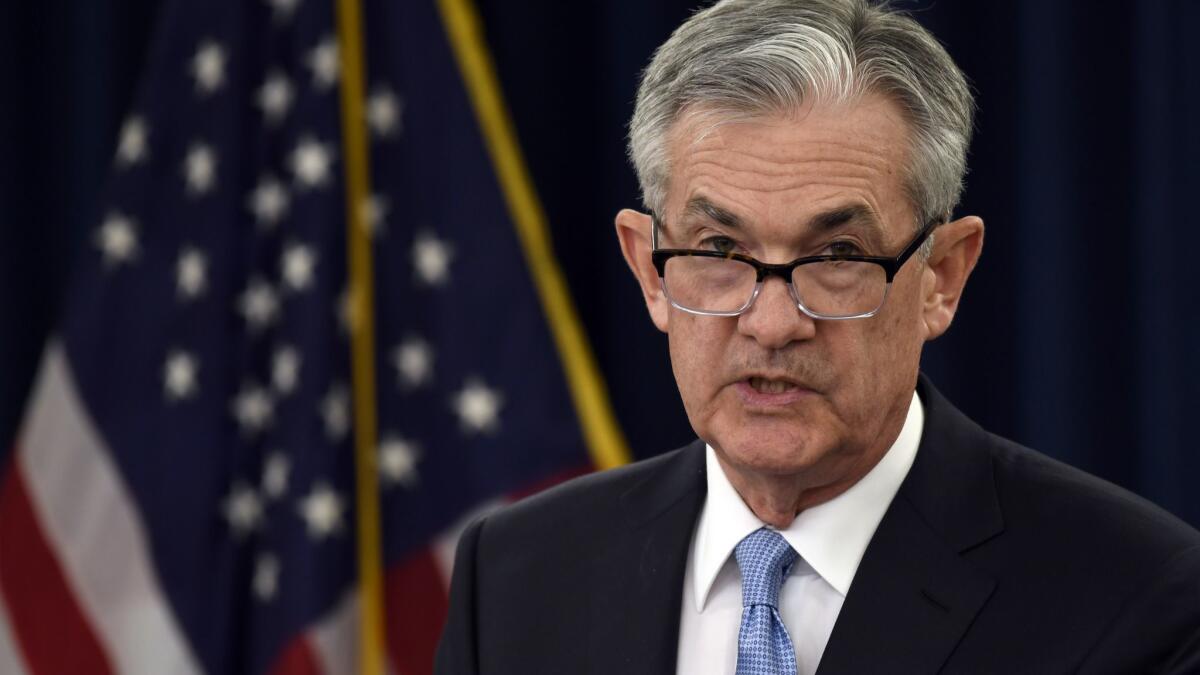

Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell said U.S. inflation is possibly being dragged down by “transitory” forces and there is no bias to either tighten or ease monetary policy.
Powell — who has been slammed by President Trump for not doing more to support the economy — told reporters Wednesday, after the Fed left its main interest rate unchanged, that the policy stance is “appropriate right now” and that “we don’t see a strong case for moving in either direction.”
The committee repeated language from its previous meeting: It “will be patient as it determines what future adjustments to the target range for the federal funds rate may be appropriate,” the Fed said in a statement Wednesday following a two-day gathering in Washington.
The unanimous 10-0 decision left the target range for the benchmark federal funds rate at 2.25% to 2.5%.
The Fed’s emphasis on subdued inflation prompted knee-jerk buying of government debt as traders added to positioning for a rate cut. However, that initial rally reversed on Powell’s comments on appropriate policy and transient inflation.
Officials also adjusted one of the tools they use to keep the federal funds rate within its target range, though Powell said the “change does not reflect any shift in the intended stance of monetary policy.”
In addition to weighing economic developments, Fed officials have endured a steady drumbeat of criticism from Trump over past rate hikes. Powell and his colleagues have said repeatedly that they’ll ignore the pressure and chart policy according to what best suits the longer-run prospects of the world’s largest economy.
As with recent economic data, the Federal Open Market Committee’s assessment of conditions had something for both hawks and doves.
Officials slightly upgraded their assessment of the economy, saying “economic activity rose at a solid rate” while “the labor market remains strong.”
That characterization followed a report this week showing consumer spending rebounded in March after a lackluster start to the year. Previous data had pointed to the consumer as a weak spot in an otherwise solid first quarter.
The economy expanded at a 3.2% annualized pace from January to March, boosted by exports and inventories growth. The labor market remains robust, with unemployment around a half-century low and wage gains near the best pace of this expansion.
Still, even with consumption intact and the labor market tightening, inflation has remained vexingly low. The Fed’s preferred price gauge climbed just 1.5% in March from a year earlier, well below the central bank’s 2% target.
In subtle changes from their last statement, officials said gauges for both overall and core inflation “have declined and are running below 2%.” That removed a line from March blaming energy prices for below-target price gains and removed a reference to core inflation being “near 2%.”
The Fed’s fears over low inflation have been mounting, with Powell recently calling it “one of the major challenges of our time.” That has spurred some speculation that a further slowing in core price gains could prompt officials to cut interest rates even during a healthy expansion.
In a supplemental statement, officials adjusted a tool they use to keep the federal funds rate within its target range, lowering the interest paid on bank reserves deposited with the Fed to 2.35% from 2.4%.
This was the third such adjustment in a year for interest on excess reserves, or IOER. As in June and December, the step was taken after the rate that banks pay to borrow overnight, known as the effective federal funds rate, drifted upward and threatened to reach the upper end of the target range.
The move “is intended to foster trading in the federal funds market at rates well within the FOMC’s target range,” the technical statement said.