Typical layout of where sensors are and how they work
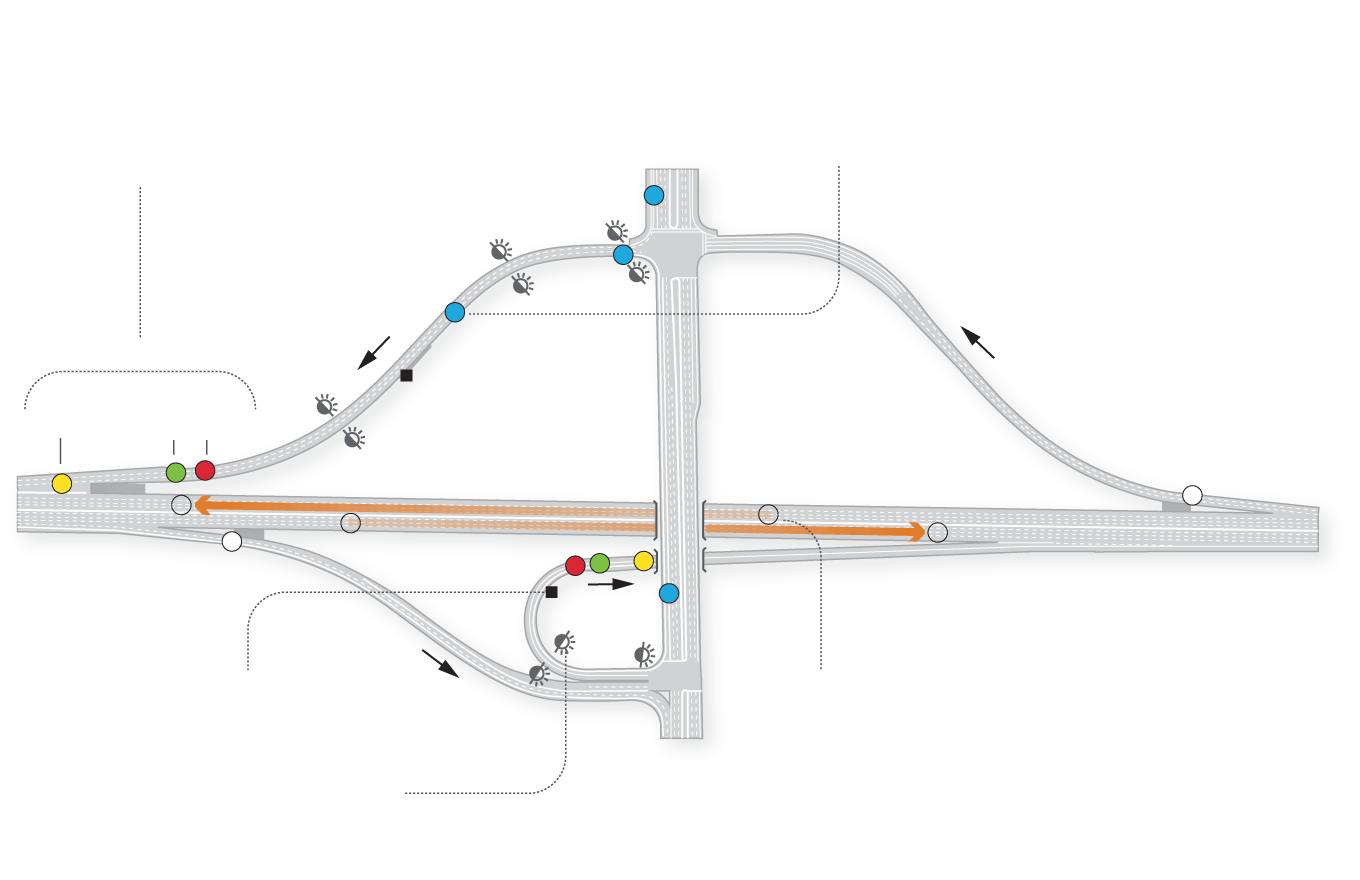
Sub-pavement sensors near the freeway entrance detect when cars are waiting to enter the freeway, trigger the timer that controls when the lights will change and count cars entering the freeway.
Queue sensors near the bottom of the on-ramp detect when the ramp is backing up and could interfere with traffic on the adjacent street.
Off-ramp
On-ramp
Detectors
Controller
computer box
Street
overpass
Counter
Passed
Waiting
Exit detector
On-ramp
Freeway
Exit detector
Off-ramp
Sensors feed real-time data to a computer controlling the meters.
Mainline sensors on freeways determine when there’s congestion by measuring how long it takes a car to travel between two sensors.
Flashing beacons indicate when meters are on.
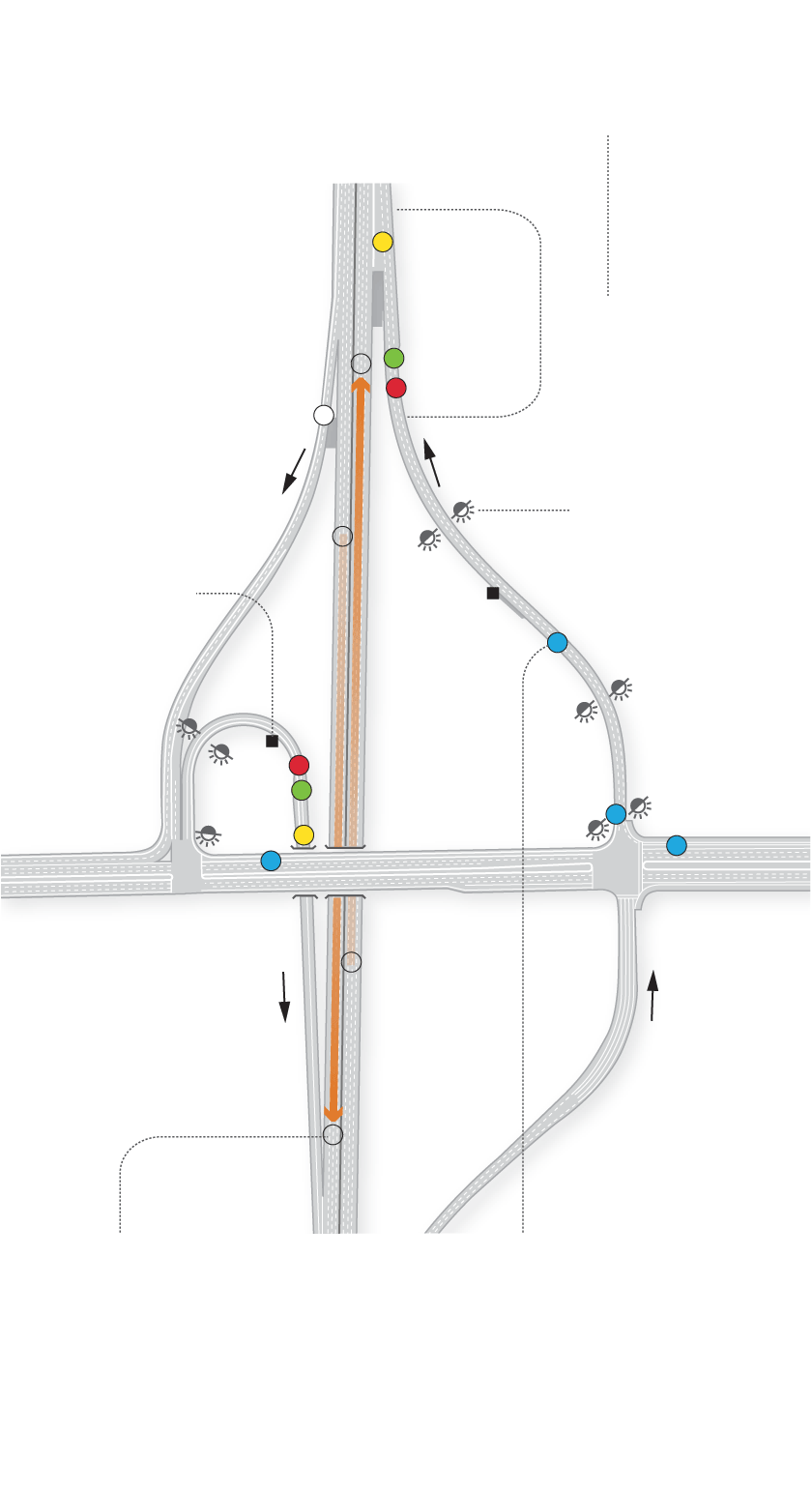
Sub-pavement sensors near the freeway entrance detect when cars are waiting to enter the freeway, trigger the timer that controls when the lights will change and count cars entering the freeway.
Freeway
Counter
Detectors
Passed
Waiting
Exit detector
Off-ramp
On-ramp
Sensors feed
real-time data
to a computer
controlling
the meters.
Flashing
beacons indicate when meters are on.
Controller
computer
box
Street overpass
On-ramp
Off-ramp
Mainline sensors on freeways determine when there’s congestion by measuring how long it takes a car to travel the distance between two sensors.
Queue sensors near the bottom of the on-ramp detect when the ramp is backing up and could interfere with traffic on the adjacent street.
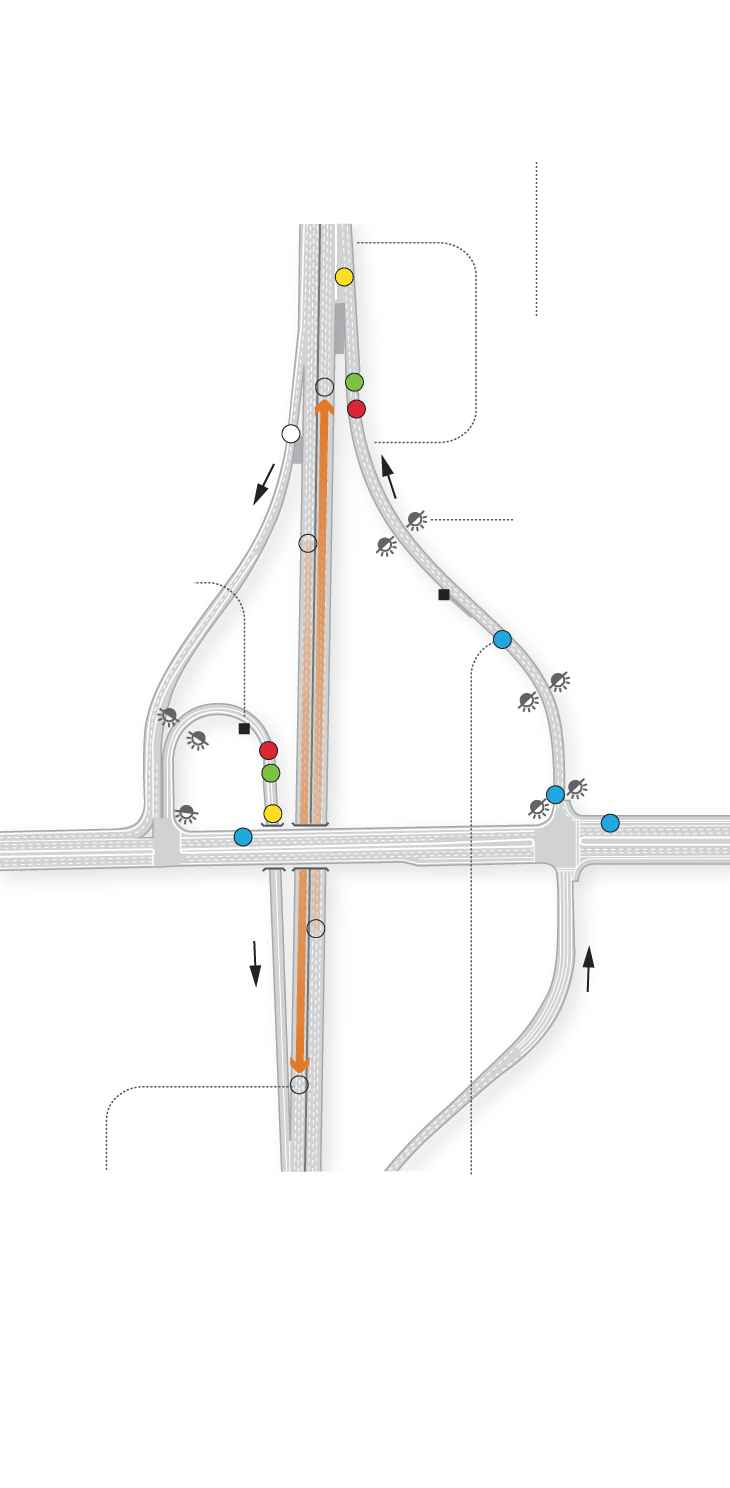
Sub-pavement sensors near the freeway entrance detect when cars are waiting to enter the freeway, trigger the timer that controls when the lights will change and count cars entering the freeway.
Freeway
Counter
Detectors
Passed
Waiting
Exit detector
Off-ramp
On-ramp
Flashing
beacons indicate when meters are on.
Sensors feed
real-time data
to a computer
controlling
the meters.
Controller
computer
box
Street overpass
On-ramp
Off-ramp
Mainline sensors on freeways determine when there’s congestion by measuring how long it takes a car to travel the distance between two sensors.
Queue sensors near the bottom of the on-ramp detect when the ramp is backing up and could interfere with traffic on the adjacent street.
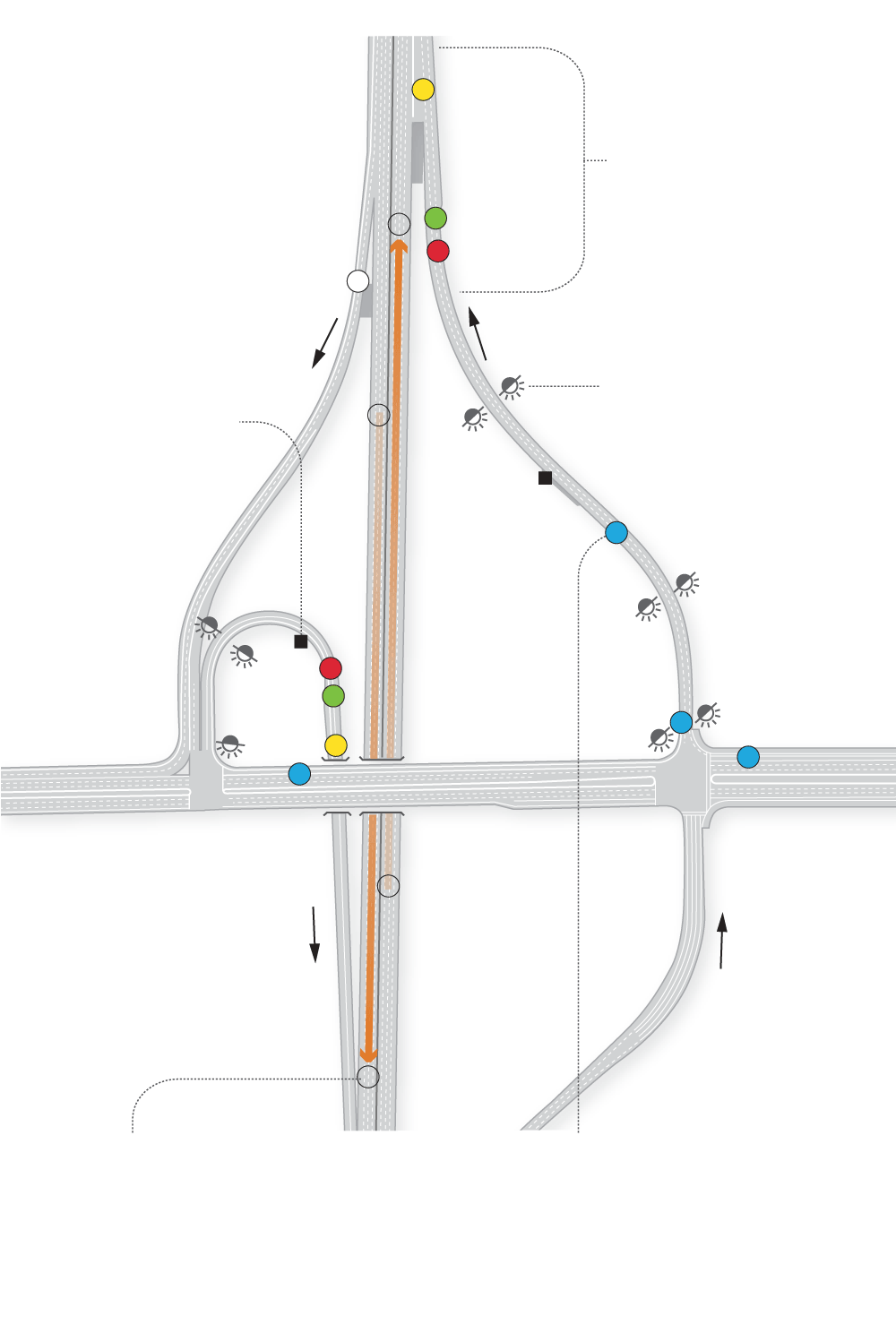
Detectors
Sub-pavement sensors near the freeway entrance detect when cars are waiting to enter the freeway, trigger the timer that controls when the lights will change and count cars entering the freeway.
Counter
Freeway
Passed
Waiting
Exit detector
Off-ramp
On-ramp
Sensors feed real-time
data to a computer
controlling the meters.
Flashing beacons indicate when meters are on.
Controller
computer
box
Street overpass
On-ramp
Off-ramp
Mainline sensors on freeways determine when there’s congestion by measuring how long it takes a car to travel the distance between two sensors.
Queue sensors near the bottom of the on-ramp detect when the ramp is backing up and could interfere with traffic on the adjacent street.
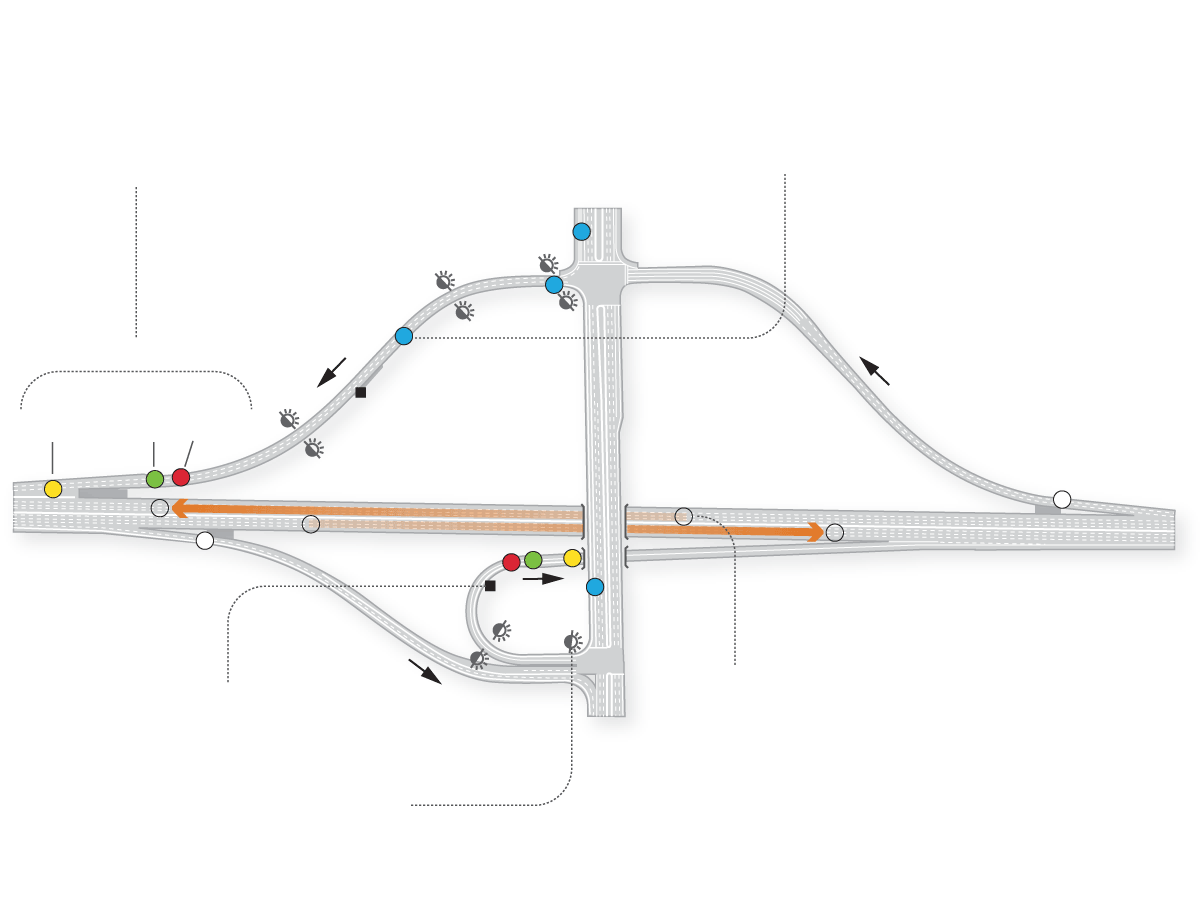
Sub-pavement sensors near the freeway entrance detect when cars are waiting to enter the freeway, trigger the timer that controls when the lights will change and count cars entering the freeway.
Queue sensors near the bottom of the on-ramp detect when the ramp is backing up and could interfere with traffic on the adjacent street.
On-ramp
Off-ramp
Detectors
Controller
computer box
Street
overpass
Counter
Passed
Waiting
Exit detector
Freeway
On-ramp
Exit detector
Off-ramp
Sensors feed real-time data to a computer controlling the meters.
Mainline sensors on freeways determine when there’s congestion by measuring how long it takes a car to travel between two sensors.
Flashing beacons indicate when meters are on.
California Department of Transportation, Times reporting
Lorena Elebee LOS ANGELES TIMES