The quiet man who harbored Islamic State leader Baghdadi
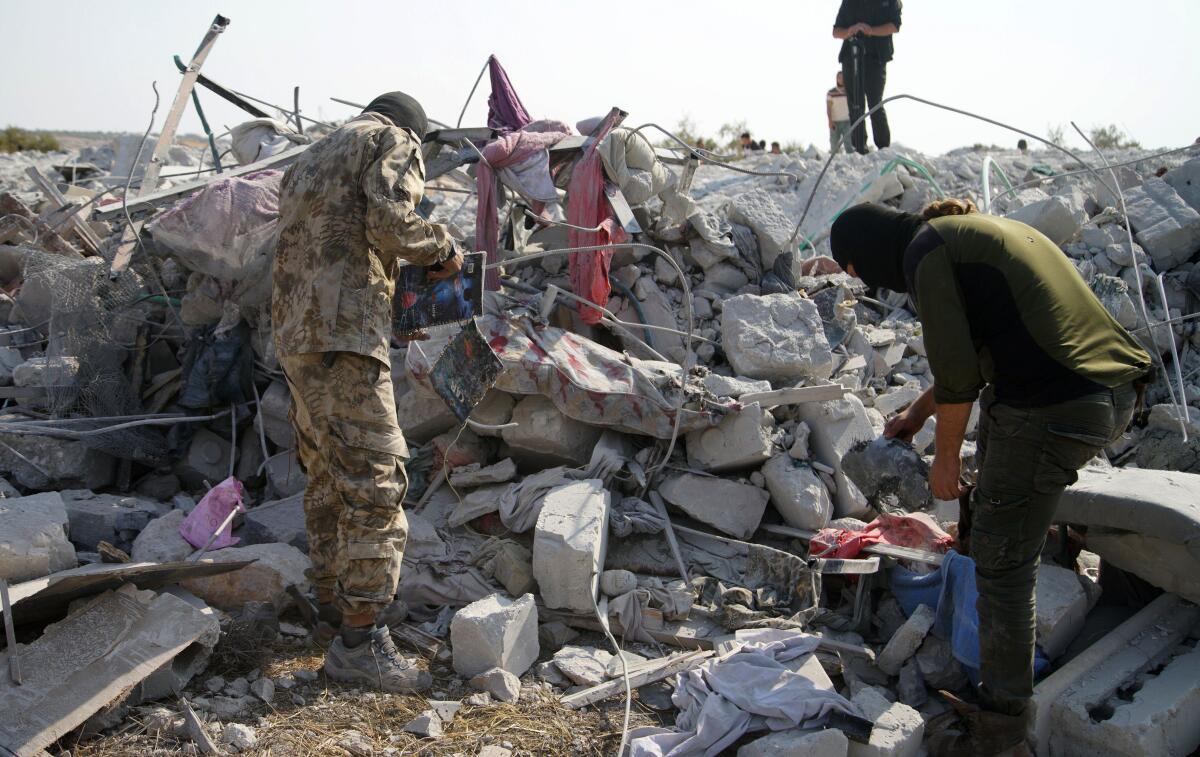

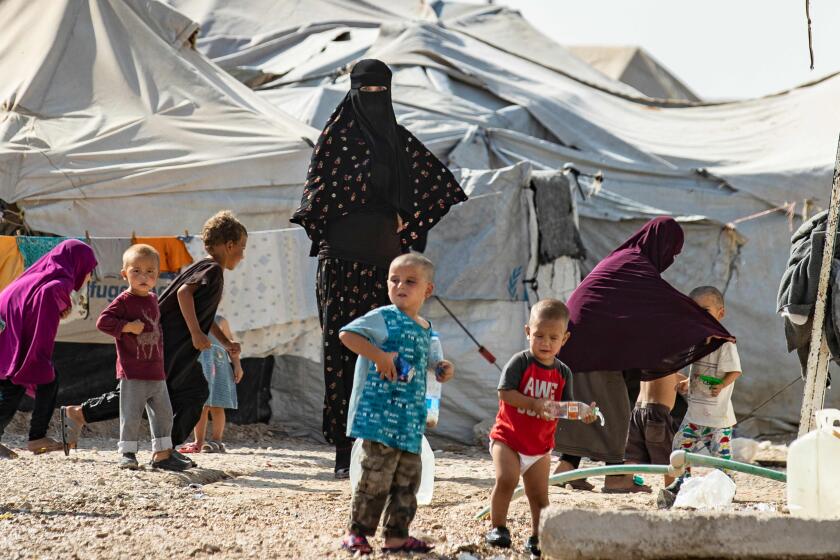
The locals knew him as Abu Mohammed Salama, an animal feed wholesaler who lived in a compound on the edge of Syria’s border with Turkey, on the outskirts of a town called Barisha. Salama was friendly enough, residents said Monday, but mostly kept to himself.
So they were surprised to learn about his secret life as the commander of an extremist group affiliated with Al Qaeda — and even more surprised to learn that he had been harboring a rival extremist, Abu Bakr Baghdadi, the founder of Islamic State.
“Who would come here — to a village with nothing?” asked Ayman Abdul Ghani, a 33-year-old medical activist working with Barisha’s local council. “Let’s be logical.”
Baghdadi died last weekend during a raid by U.S. forces on the compound in Barisha, according to President Trump and other U.S. officials. Trapped in a tunnel on the property, Baghdadi blew himself up, killing three children in the process. Salama, which was believed to have been a pseudonym for Abu Mohammed Halabi, the leader of the extremist group Guardians of the Religion, was also cut down in the raid, residents say, and his body was taken away by the special operatives.
His reign was marked with bouts of genocidal reengineering of communities that didn’t fit his vision for a Sunni Muslim state.
In the aftermath of the raid, questions remain about how Baghdadi came to the squat compound, where Salama had lived with his eight children for three years.
Barisha, about 30 miles west of the city of Aleppo and a few miles south of the border with Turkey, had largely escaped the punishing air campaign waged by Syrian and Russian warplanes over northern Syria in recent years, mostly because it was so unimportant.
That quiet was punctured just before 11 p.m. Saturday, when helicopters swarmed over Salama’s house. Rapid cracks of machine-gun fire and tracer rounds flared in the sky.
“There was just shooting everywhere. We heard someone on the ground shooting at the helicopters, then they responded. We just started panicking,” said Alaa, a 33-year-old worker with the local council who gave only his first name for fear of reprisals.
Though Alaa’s house was more than 400 yards away, when he went to his window to see what was happening, a bullet pierced the thick frosted glass, smacked into a picture hanging on the wall and sent a shower of shards on his children.
“We didn’t even dare turn on our lights to see what was happening,” said Alaa.
Later, a shepherd living in a tent next to Salama’s house (he too had only exchanged greetings with Salama) brought eight children, all younger than 10, to Alaa’s neighborhood, Alaa said. The shepherd said that they had been handed to him by the operatives storming the compound and that he was to take care of them.
The children, Alaa said, were now with the authorities who control surrounding Idlib province, which is the last part of Syria still held by forces opposed to Syrian President Bashar Assad. Syria has been torn by civil war since 2011, although Assad, with Russian and Iranian help, is now back in control of most of the country.
The same opposition forces had also been fighting against Islamic State, adding to the mystery of how Baghdadi wound up in Salama’s house in Barisha.
Before the civil war, the village had been virtually abandoned, Abdul Ghani said in a phone interview. Most people left to find work elsewhere in the country, he said. Those who did stay worked in the sparse olive groves, or the small wheat fields near ancient Roman ruins. It was the civil war that brought many of its original inhabitants back, swelling the village’s population from less than 1,000 before the war to 12,000.
About 4,000 of Syria’s displaced had also settled in Barisha, many of them poor people unable to afford living elsewhere or who wanted to be near the Turkish border.
Salama was thought to have come as one of those internally displaced, Alaa said.
“He came almost three years ago, bought a house that was still under construction, finished it and put a fence around it,” he added. Salama also enrolled his children in the school, and seemed to have no qualms about being seen, though he rarely had visitors, except to hook up internet service or refill his water tanks.
Though services were few, said Abdul Qader Abdul Ghafour, the top civilian administrator in Barisha, the area was controlled by a onetime Al Qaeda affiliate known as the Committee for the Liberation of Syria and was thought to be secure. Although Baghdadi had once been an Al Qaeda member, he broke away from the group when he formed Islamic State and the two groups had become sworn enemies.
“If we had known this person was here, of course we would have captured him,” Abdul Ghafour said in an interview Monday.
The hunt for Baghdadi had begun well before Islamic State lost the last of its territory this year. At its zenith, the group controlled an area roughly the size of Britain, with anywhere from eight to 12 million people under its rule.
As Islamic State was squeezed between rival U.S.-led and Russian-supported campaigns, teams of special operatives and spies roamed the group’s onetime bastions to track down Baghdadi. Reports would breathlessly declare he was killed in an airstrike or wounded and dying, but there was never confirmation.
After the U.S.-led coalition declared victory over the group this year, there was no sign of him, save for a few audio and video recordings in which he vowed Islamic State would still fight.
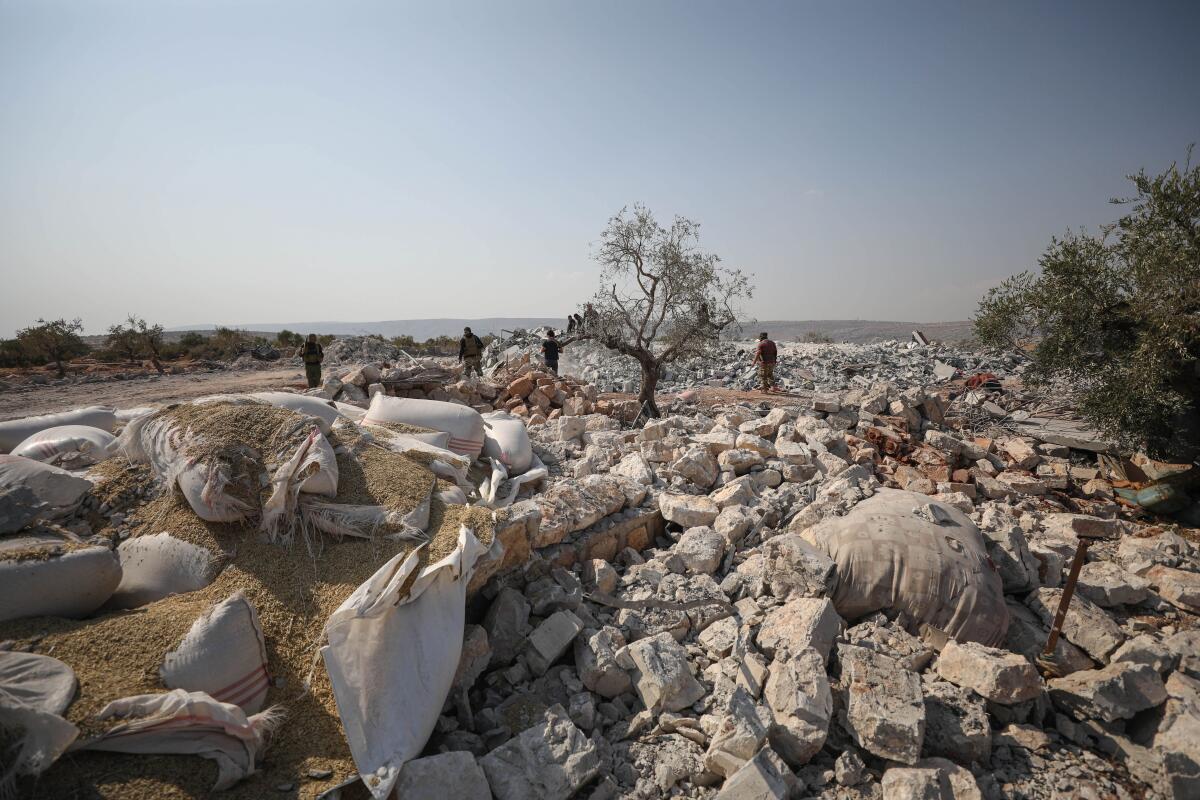

To reach Barisha, Baghdadi would have had to traverse hundreds of miles, through desolate deserts as well as urban centers and major highways, from the group’s stronghold in the northeast. If he had gone through Syria, he would have had to navigate a Swiss-cheese landscape of influence and control by groups of different loyalties, including the Syrian government and its allies, as well as opposition and Islamist factions.
A senior U.S. State Department official described Idlib province as a chaotic mishmash of competing groups. “It is as messy a mix as you have in northeast Syria,” the official said.
It was also possible Baghdadi wanted to remain near the Turkish border. In the early days of Islamic State’s formation, that border had been the conduit for the tens of thousands of fighters who came from 100 countries to join its ranks.
Turkey, amid increasing pressure from the U.S. and a growing Islamic State threat in its own territory, finally sealed the border. Yet many militants were thought to have escaped to Turkey during Islamic State’s slow demise.
Baghdadi could also have blended in with the many Iraqi families, refugees who fled either with or from Islamic State into Syria. Many of them now live in camps in the steppes of the country’s north. Idlib province, commentators say, is infiltrated by Islamic State sleeper cells more than willing to hide their caliph.
Some say Salama was part of such a cell. Whatever his loyalties were, opposition activists reported that Salama was more than a wholesaler. Barisha residents were trying to reconcile that with the friendly man they knew.
“He was like any other refugee,” Alaa said.
Times staff writer Patrick J. McDonnell in Qamishli, Syria, contributed to this report.
More to Read
Start your day right
Sign up for Essential California for news, features and recommendations from the L.A. Times and beyond in your inbox six days a week.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.