Americans adjust to a changed role in Iraq
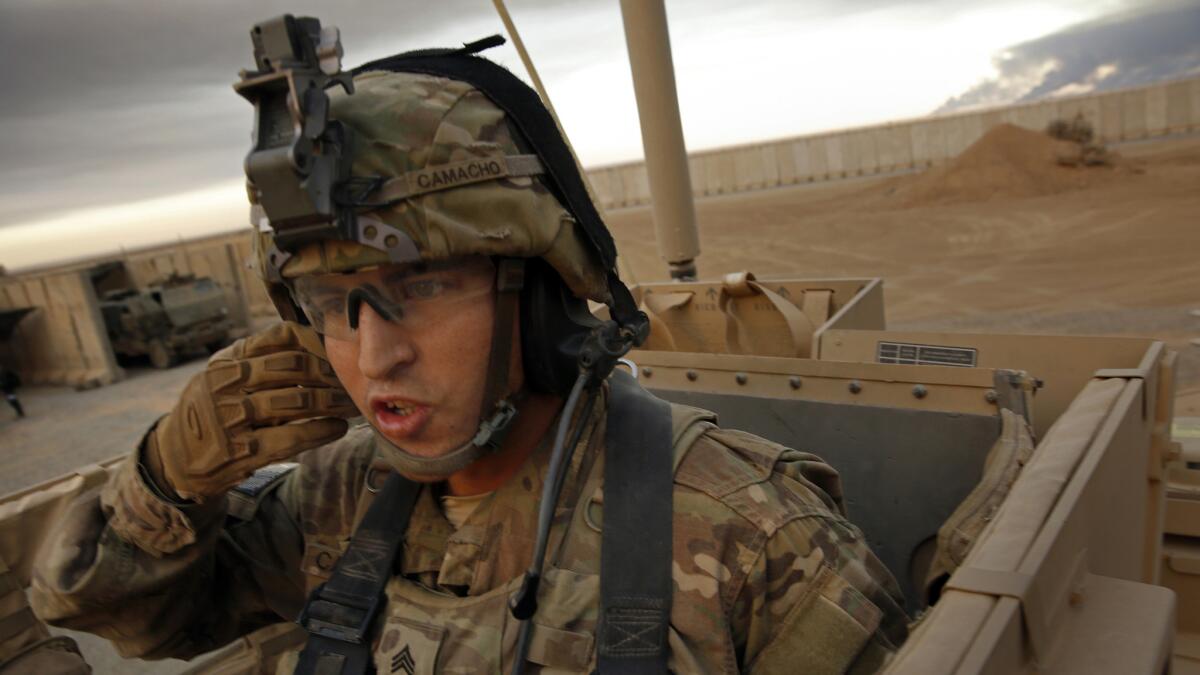

By the time Iraqi forces recaptured this sprawling airfield once known as “Key West” from Islamic State last summer, the militants had ruined everything: The Olympic-size pool, the track, the PX store, dining hall, even the runways, plowed under and rendered unusable.
But it was a significantly changed scene that U.S. Air Force Col. Rhett Champagne surveyed last week as he stood on the main landing strip, his radio buzzing with news of an Iraqi C-130 preparing to land and load supplies for the battle to retake the city of Mosul from Islamic State.
Qayyarah West Airfield, more commonly known as “Q-West,” has become a nerve center for the operation at Mosul, 40 miles north, and a headquarters for U.S. troops who are advising the Iraqi Army in their effort to defeat the militant jihadi organization.
“ISIL did its best to make Q West somewhere the coalition couldn’t support the Iraqis,” Champagne said of the jihadis. “They failed.”
When U.S. forces withdrew from Iraq in 2011, many expected never to return. President Obama described the country as “sovereign, stable and self-reliant.” But after Islamic State swept across Iraq and Syria, capturing Mosul in 2014, the Iraqi government once again sought help.
More than 5,200 U.S. troops are now assigned to a non-combat “advise and assist” role in Iraq, arrayed from Q West, Camp Swift and Irbil in the north to Al Asad Air Base in the west, and further south, in Baghdad. Near the front lines, Iraqi militias are being trained by U.S. special forces.
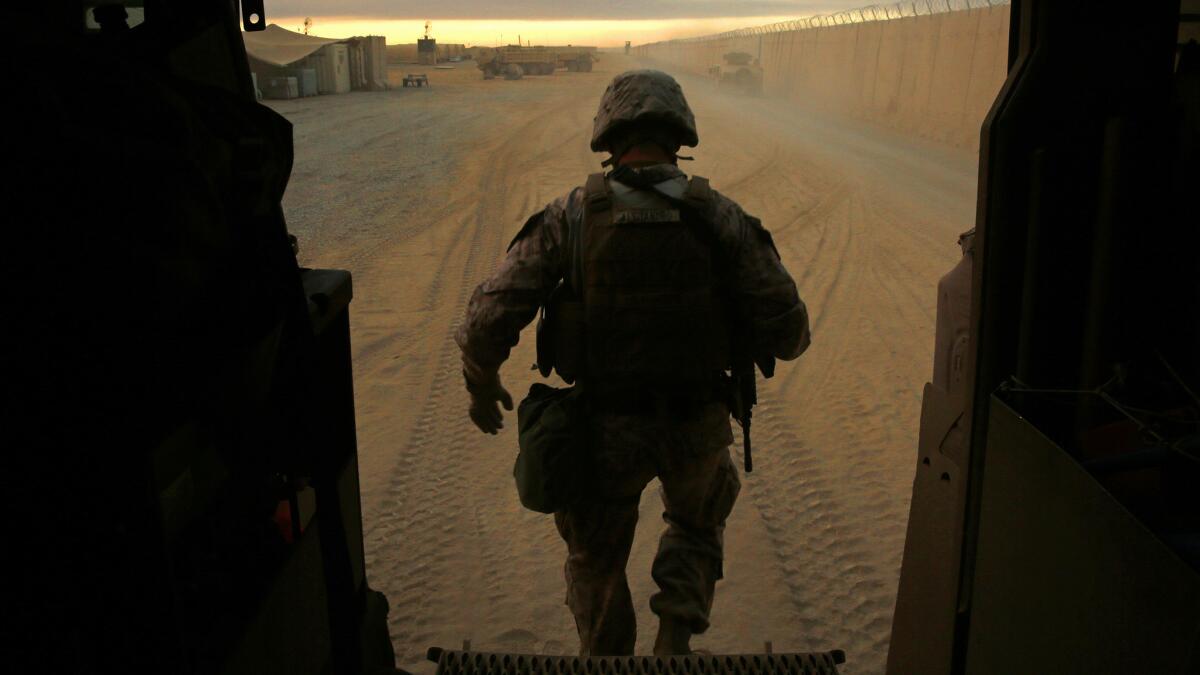

The role of U.S. forces in the Mosul offensive is a tricky one, the boundaries delicate.
“We’re doing some stuff you don’t normally do, especially the integration with Iraqi counterparts,” Champagne said, adding that the mission requires cooperation, patience, and a willingness to recognize that, “The Iraqis are capable. They’re going to solve their problems their own way.”
When Champagne, 45, went to work one recent night, he heard sobering news from an Iraqi commander.
“He hasn’t seen his mom in Mosul in two years,” Champagne said from a tent surrounded by airmen from his 821st Crisis Response Group at Travis Air Force Base in Northern California. “That kind of puts it in perspective.”
For troops like Staff Sgt. Thomas Morris returning to Iraq, the changed role has been a challenge.
Morris, 34, whose platoon includes mostly young soldiers on their first deployment, tells stories about the first time he came to Iraq in 2004: eating steak and lobster at massive U.S. bases in Baghdad, swimming in pools at former Iraqi leader Saddam Hussein’s former palaces, patrolling in Humvees and kicking in doors.
“Pretty much every time out you got contact. Our battalion got pretty lucky: We only lost seven or eight guys,” said Morris, 34, of Baltimore.
He wasn’t sure how to behave around Iraqi soldiers he met at the airfield convenience store, Sami’s. Some would ask to take photos with him, others to trade gloves. Morris kept thinking: “Their fathers and grandfathers were probably fighting against the United States.”
“We knew we weren’t coming back as an occupying force, but when we got back here it was a little eerie,” he said last week as he stood near a sign marking “Rocket City.” His unit and Iraqi soldiers take turns firing into Mosul.
Air Force Tech. Sgt. Corey Blakely was also stationed in Iraq in 2004 at Balad, a base that was attacked four to five times a day, earning it the nickname, “Mortaritaville.”

We take a look at the role of U.S. forces in the fight for Mosul, Iraq — a battle in which they have no direct role. Yet they are everywhere. (Video by Molly Hennessy-Fiske / Los Angeles Times)
Now Iraqi forces fly helicopters into an airfield pocked with bullets from combat, then immediately return to the fight, their leaders coordinating airstrikes from a joint command center.
“You can see how everything is turning back over to the Iraqis,” said Blakely, 38, of Boston. He and others say they are happy that their work keeps them mainly on base.
But it can be difficult to explain their changed role to friends and family back in the U.S. who see footage of gunfights in Mosul and assume they are out battling Islamic State.
“People want to know how many kills you have,” said Tech. Sgt. Christopher Queen, 41, of Merced.
Soldiers who drive off the base on security patrols see Iraqis returning home to nearby towns after being displaced by fighting.
“It went from ghost towns to people moving back in. Now there’s kids playing,” said Army Staff Sgt. Josh Hogue, 26, of Sutter, Calif., with the 101st Airborne Division based at Ft. Campbell.
Army Capt. Alex Carlier, who served in Afghanistan, said he has all the soldiers and equipment he used to have to compete for and faces fewer risks.“Nothing is risk-free, but it’s very mitigated,” said Carlier, 29, of Columbus, Ohio, as the boom of outgoing rockets sounded.
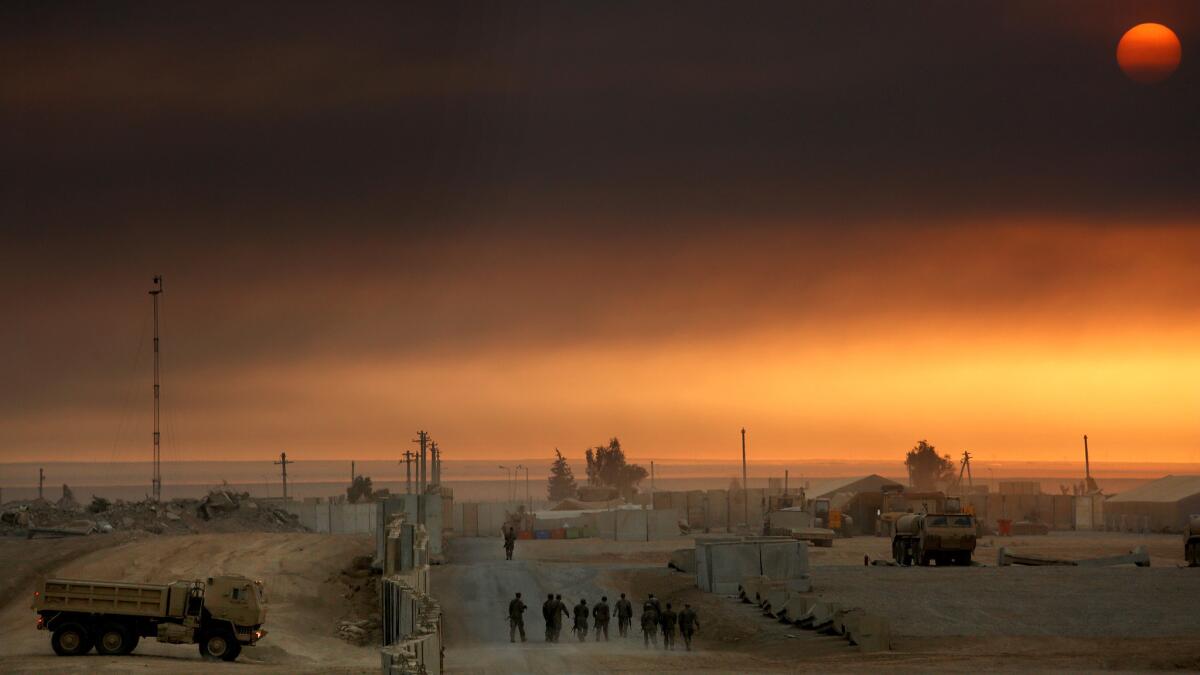

Iraqi commanders said they are grateful for U.S. support, that they have enough ground troops but could not have entered Mosul so rapidly without coalition airstrikes and technical help.
“Without the support of the Americans, the operation would be slower,” with more casualties, said Iraqi Brigadier General Firas Bashar, speaking from a tent on the Iraqi side of Q West.
Outgoing artillery sounded, fired by U.S. service members on the base toward an Islamic State stronghold near Mosul. Bashar smiled.
“That’s the American support we’re talking about,” he said.
Maj. Gen. Najim Jabouri, commander of the Mosul operation, said Iraqi forces need to lead the offensive “because this is our home,” but U.S. military technology has paved the way.
“They have the drones, the bombs that are very specific, like a surgeon with the cancer,” Jabouri said.
First Lt. Zelly Zim’s team flies several observation drones over Mosul, screens their video feed and coordinates with Iraqis to target suicide bombers and other militants.
“Our soldiers will see something on the feed and very quickly will go to the Iraqis so there can be a strike,” sometimes in minutes, said Zim, 24, of Fairfax, Va.,who called it “the purest form of my job.”
Staff Sgt. Steven Ramos, 26, of Yorba Linda was excited about his first deployment here, hoping to collect war stories. And he has, working the airfield with Iraq counterparts.
“You look on the other side of the berm and you see all these fires. You hear the stories of these airfield workers that have family in Mosul and haven’t seen them for years at a time. This is why they’re here,” he said.
Hearing the Iraqis’ stories made Ramos think about California.
“It’s hard knowing we’re living completely different lives. Coming from Orange County — the beach is 20 minutes away — to these families, who haven’t seen their mother, their father, their brothers, for years or months,” he said.
He wasn’t sure at first how to respond.
“I can’t tell them that I’ve been there before. I can’t tell them I know what it’s like,” he said.
All he could say was that he came to help.
molly.hennessy-fiske@latimes.com
Twitter: @mollyhf
ALSO
Syrian government and rebels blame each other for Aleppo evacuation chaos
Fears of Russia and Trump drive EU leaders to boost defense budgets
China seizes U.S. underwater drone in South China Sea, prompting a formal complaint
More to Read
Start your day right
Sign up for Essential California for news, features and recommendations from the L.A. Times and beyond in your inbox six days a week.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.