Optimism as Omicron peaks in California, but new BA.2 subtype raises questions
There is growing optimism that the overall Omicron surge has peaked in California, but progress across the state remains uneven.
The improvement is most pronounced in places like Los Angeles County and the San Francisco Bay Area, where health officials have voiced increased confidence in recent days that the coronavirus test positivity rate, and daily new coronavirus cases and hospitalizations have either stabilized or begun to convincingly decline.
“This downward trend is encouraging, and it signals that we’re likely to have passed the peak of Omicron transmission and are beginning to see a real decline in the number of newly infected individuals,” L.A. County Public Health Director Barbara Ferrer said.
One potential wrinkle, though, is the emergence of a subtype of Omicron.
The World Health Organization has said the appearance of the subtype, called BA.2, is increasing in many countries. Two cases have also been found in Santa Clara County, Northern California’s most populous county.
“We don’t really know what that means yet. We’ll be learning that in the days and weeks to come,” said Dr. Sara Cody, the county’s health officer and public health director. “So far, we don’t really know how it behaves.”
There remains considerable debate about the pandemic’s trajectory, but scientists generally say it’s too early to declare an ‘endgame’ for COVID-19.
Dr. Peter Chin-Hong, a UC San Francisco infectious-disease expert, said Wednesday that there’s nothing in the early data right now that makes him worried about BA.2.
“And the reason why I’m not worried is because I’m confident that, if you get boosted ... you wouldn’t go to the hospital,” Chin-Hong said. “I’m not worried about it as being more deadly,” he said, based on early data out of Denmark, but added that he’s “keeping an open mind. You never know what’s going to happen. It has a few more mutations. But I’ll be shocked if it makes you sicker.”
BA.2 will still be a risk for infecting people who haven’t been vaccinated and haven’t had prior exposure to Omicron. “I think our vaccines and our boosters will still work,” Chin-Hong said.
Cody said she thinks more coronavirus waves are yet to come, but it’s unclear what the next one will look like — whether it will be something little or another huge mountain.
“The road ahead still has a lot of uncertainty. We don’t know what’s going to come next,” Cody said at a town hall Tuesday night. “The greatest challenge for all of us is that we can’t quite see around every corner.”
Dr. Anthony Fauci, President Biden’s chief medical advisor, said this week that he doesn’t expect that the pattern of huge challenging variants emerging twice a year will last forever.
“What likely happens when you have waves of this is that, after a while, there is enough background immunity — either from infection-plus-boost, or vaccine-plus-boost, or just plain infection-and-recover-from-infection — when you put it all together, you can have a degree of immunity in the community such that, even if new variants emerge, they don’t take that surge effect that we’ve seen with the … five surges that we’ve seen since early 2020,” Fauci said on MSNBC on Tuesday.
“So I don’t believe we’re going to be seeing that indefinitely,” Fauci said. “I think it’s going to come down and down. And quite frankly, the more people that we get vaccinated and the more people we get boosted, the less the likelihood that we’ll be seeing these return of variants that keep challenging us.”
Face masks will be given to Super Bowl spectators at the Inglewood stadium for the game, which is a little more than two weeks away.
Even as case numbers improve, officials continue to urge caution.
Case numbers “are still extraordinarily high,” and “there continue to be a significant number of people in L.A. County with severe illness,” many of whom are unvaccinated, Ferrer said.
“Omicron was an eye-opener, in part because people who had gotten infected with Delta seem to have almost no protection against Omicron,” Ferrer said Tuesday. “And I don’t think Omicron is our last variant.”
While it’s true that unvaccinated people who survive Omicron are going to have some natural immunity to the variant, there’s also evidence that doesn’t last long, Ferrer said.
“We seem to have the science telling us we’re all getting the better protection, obviously, from our vaccines and our boosters,” she said.
Chin-Hong agreed that natural immunity hasn’t been enough to protect people from re-infection. “Immunity from Delta doesn’t protect you from Omicron,” he said.
People who have survived a previous bout of coronavirus infection, but still decline to get vaccinated, will be at risk for future infection as natural immunity weakens. “They will continue to be at risk because they will run out of gas,” Chin-Hong said of their immunity, similar to how a partially vaccinated person is at higher risk for infection.
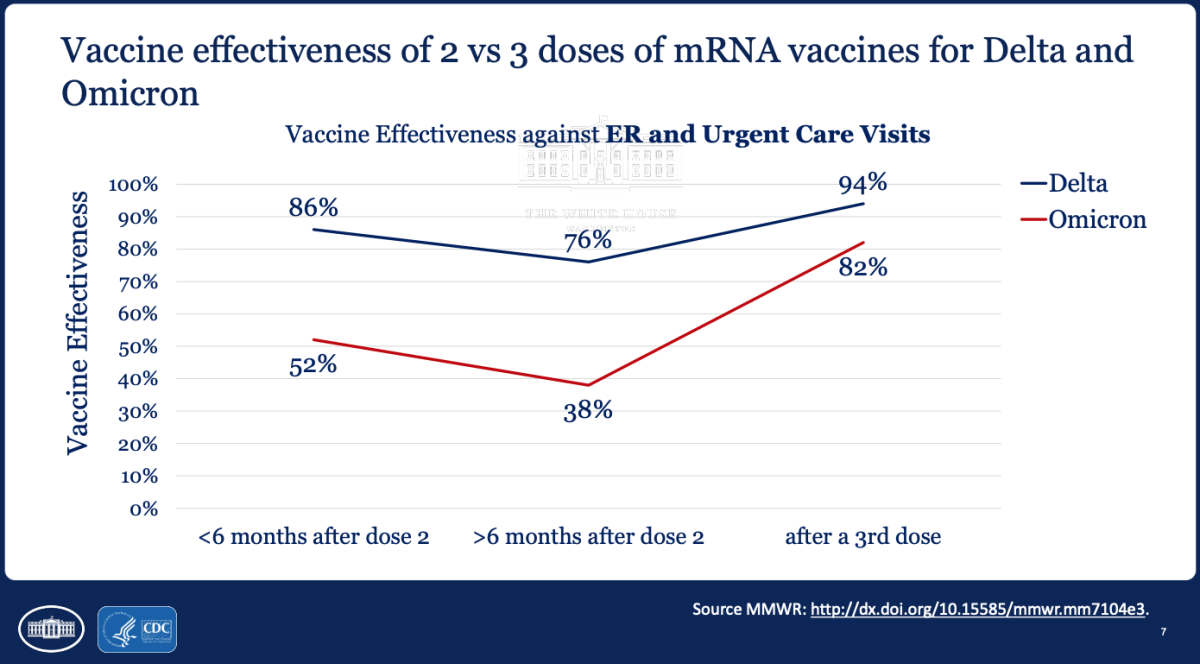
Emerging data show that booster shots confer significant vaccine effectiveness against visits to the emergency room. Against Omicron, vaccine effectiveness against emergency room and urgent care visits more than half a year after the second dose of a Pfizer or Moderna shot is only 38%. But after a booster shot, vaccine effectiveness rises to 82%.
California’s Omicron surge appears to have peaked in the week of Jan. 10-16, when the state was recording about 122,000 new coronavirus cases a day. That figure has since dropped to 94,000 cases a day, according to state data released Wednesday that reflect cases reported through Tuesday.
Still, the most recent rate remains roughly double the peak of last winter’s surge, which maxed out at 46,000 cases a day.
Statewide, the number of coronavirus-positive hospitalizations has also stabilized in recent days and is no longer increasing dramatically. On Jan. 19, L.A. County recorded 4,814 patients — about 60% of last winter’s peak of 8,098. As of Tuesday, that census had fallen to 4,534.
Omicron’s transmissibility has been so breathtaking in scope, it’s hard to grasp just how many more Californians have been simultaneously infected over the last month.
Since New Year’s Day, a staggering 2.5 million coronavirus cases have been reported in California. That’s fast approaching the entire sum of coronavirus cases reported statewide all of last year: 3.1 million.
A bill that would require California school kids to be vaccinated raises debate over parent rights and the role of the government, among other matters.
Compared with their Omicron peaks, daily coronavirus case rates have dropped by 32% in L.A. County, 35% in Orange County, 25% in San Bernardino County and 20% in Ventura County, according to a Times analysis of state data released Wednesday.
Regionally, Southern California, the San Francisco Bay Area and the Greater Sacramento area have also observed declines of roughly 25%.
“We are past the peak,” said Cody, the Santa Clara County health officer. “And we’re just beginning to see early signs that our hospitals may be seeing a little bit of a reprieve.”
“It’s been an extraordinarily difficult several weeks. But I think that spread is beginning to come down. That being said, it’s, of course, still quite high,” Cody said.
Yet the San Joaquin Valley and rural Northern California have yet to begin a persistent drop. In Southern California, San Diego and Riverside counties have also yet to observe the same.
L.A. County reported the highest single-day tally of COVID-19 deaths since March 2021 on Thursday.
The Omicron wave has exacted a deadly toll. In recent days, L.A. County has averaged about 60 COVID-19 deaths a day over a weekly period, a rate that exceeds all past surges except for last winter’s.
While much has been made of Omicron’s seemingly milder nature compared with other variants, Ferrer urged people to do all they can to avoid infection. That includes avoiding nonessential gatherings, especially in indoor settings where masks are not worn, such as restaurants and bars.
Doing so, she said, will help protect vaccinated people from breakthrough infections and vulnerable people — such as the elderly, those with underlying health conditions and children too young to be vaccinated — from illness.
“While we’re finally turning the corner in the surge, we do need to remain cautious in order to reduce transmission to a low enough level that imposes less risk for those most vulnerable,” Ferrer said. “The continued high rate of transmission creates a lot more risk.”
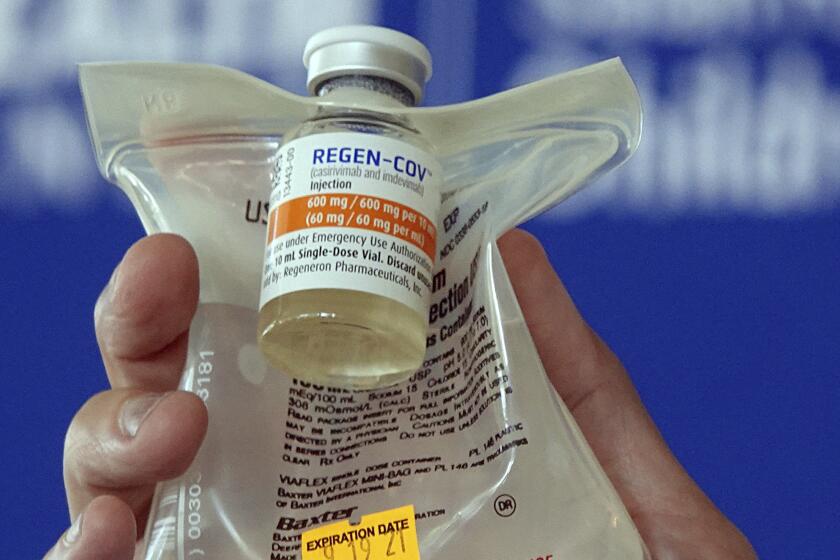
U.S. officials say COVID-19 antibody drugs from Regeneron and Eli Lilly should no longer be used because they don’t work against Omicron variant.
Challenges remain. While 3 million L.A. County residents have received booster shots, another 3 million eligible people haven’t yet. That’s a problem, because “we continue to see that the booster significantly reduces COVID-19 cases, hospitalizations and deaths, particularly with Omicron,” Ferrer said.
Unvaccinated people are twice as likely to get infected compared with people who’ve been vaccinated but not yet boosted, Ferrer said. But a booster provides more protection. Unvaccinated people are four times more likely to be infected compared with those who have received their booster shot.
Unvaccinated people are also six times more likely to be hospitalized compared with vaccinated but not yet boosted people, and 24 times more likely to be hospitalized than those who have gotten boosted, Ferrer said.
Only a very small number of fully vaccinated people are dying of COVID-19, Ferrer said. Unvaccinated people are 15 times more likely to die of COVID-19 compared with fully vaccinated people.
An Israeli panel said research shows a fourth COVID-19 shot provides three to five times as much protection against serious COVID-19 as three doses.
Health officials are especially concerned about low vaccination rates among children ages 5 to 11. In L.A. County, just 30% of children in this age group have received at least one dose of vaccine. In the poorest neighborhoods, only 22% of these children have received at least one shot, while in wealthier areas the share is 44%.
There are also racial and ethnic disparities. In this age group, just 16% of Latino and 17% of Black children have received at least one dose of vaccine, compared with 37% of white, 45% of Native American and 53% of Asian American children.
L.A. County’s immunization rates are far behind those of San Francisco, where 71% of children ages 5 to 11 have received at least one dose of vaccine.
“Regrettably, this disparity can lead to higher rates of spread and illness in the very communities that have already been hardest hit by the pandemic,” Ferrer said.
California officials hope the return of state-mandated COVID-19 sick pay will encourage infected workers to stay home and help slow transmission.
The county has dispatched the vast majority of its hundreds of scheduled mobile vaccination events into communities with the fewest resources, Ferrer said.
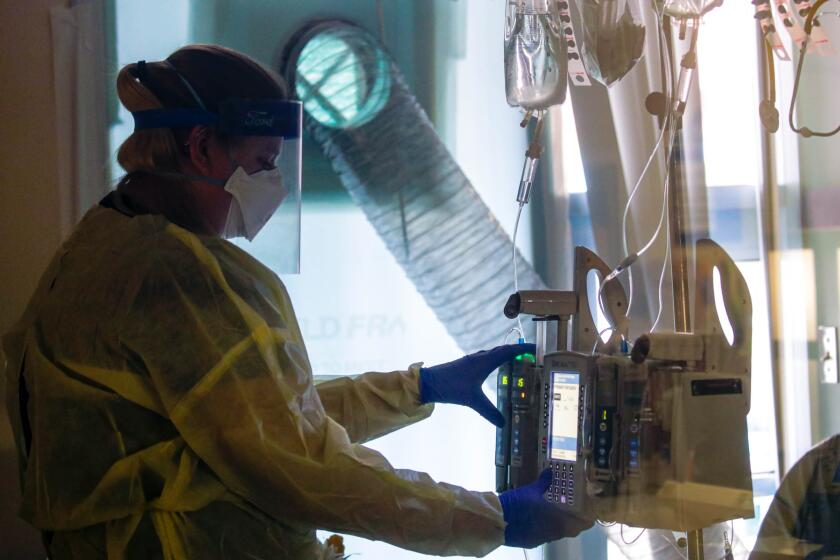
Even though hospitals in L.A. County are no longer reporting sustained increases in coronavirus-positive hospitalizations, the facilities remain challenged.
“Hospitals are still under immense stress due to staffing shortages,” L.A. County Health Services Director Dr. Christina Ghaly said.
In the last couple of months, hundreds of licensed county nurses have been temporarily unable to work because of coronavirus-related isolation or quarantine periods.
That said, the county’s public hospital system has not had to declare a crisis and hasn’t used the option of sending asymptomatic, infected health workers with active coronavirus infections back into work, despite a state rule allowing hospitals to do so in critical situations. The county has been able to procure nursing help from the state and federal government, redeploying nurses in outpatient areas into the hospital, accelerating hiring and hiring temporary nurses.
“Even with these efforts, we have a shortage of nurses that are needed to open all of our available beds,” Ghaly said. There are about 200 inpatient beds closed because of staffing shortages across L.A. County’s four public hospitals, which have been forced to postpone a number of surgeries and procedures.
A parent who recorded the tirade said the man also coughed on the group of middle schoolers. Parents say he has repeatedly harassed their kids.
Hospitals are also continuing to face difficulties in transferring recovering patients elsewhere, such as facilities that take in mental health patients, Ghaly said.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.