Alzheimer’s Warning Signs and Help Lines
- Share via
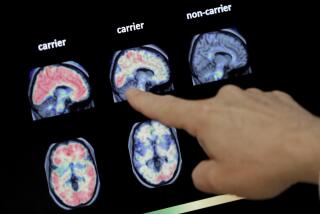
Alzheimer’s disease, the most common cause of dementia, affects an estimated 4 million Americans. It will strike one in 10 of those 65 and older, and half of those 85 and older.
The neurological disease usually begins with forgetfulness and the inability to remember familiar skills, such as balancing a checkbook. It progresses to serious memory loss, disorientation, confusion and irritability as well as changes in behavior, such as a tendency to wander. Over time, the disorder destroys brain function, eventually eliminating the ability to walk, speak or take care of personal needs.
A comprehensive medical evaluation, including a detailed medical history, physical exam, neurological exam, psychiatric assessment and laboratory testing can distinguish it from other memory-impairing disorders, such as depression and vascular dementia or other illnesses that may potentially be reversible.
There is no cure for the progressive disorder, but doctors have a limited number of medications to treat the memory loss. Often, they can treat some of the behavioral problems and depression that may accompany Alzheimer’s.
Family and friends who care for Alzheimer’s patients can seek help from local groups, such as the Alzheimer’s Assn. The association has a statewide toll-free line, (800) 660-1993, where callers can get information about the chapter nearest them, referrals to support groups (including some in foreign languages), and adult day-care centers. Printed materials in other languages are also available. The Los Angeles chapter has a Spanish-language line, (800) 633-5767, and a direct-help line, (323) 938-3370.
For those with access to the Internet, the National Alzheimer’s Assn. maintains a Web site that includes information on the disease, recent research, as well as fact sheets and caregiving tips at: https://www.alz.org. For local information, try the Los Angeles chapter Web site at https://www.alzla.org.
For Alzheimer’s disease information in Chinese, try the Web site of the Alzheimer’s Assn. of Australia. Go to the home page at https://www.alznsw.asn.au, then click on the Chinese link.