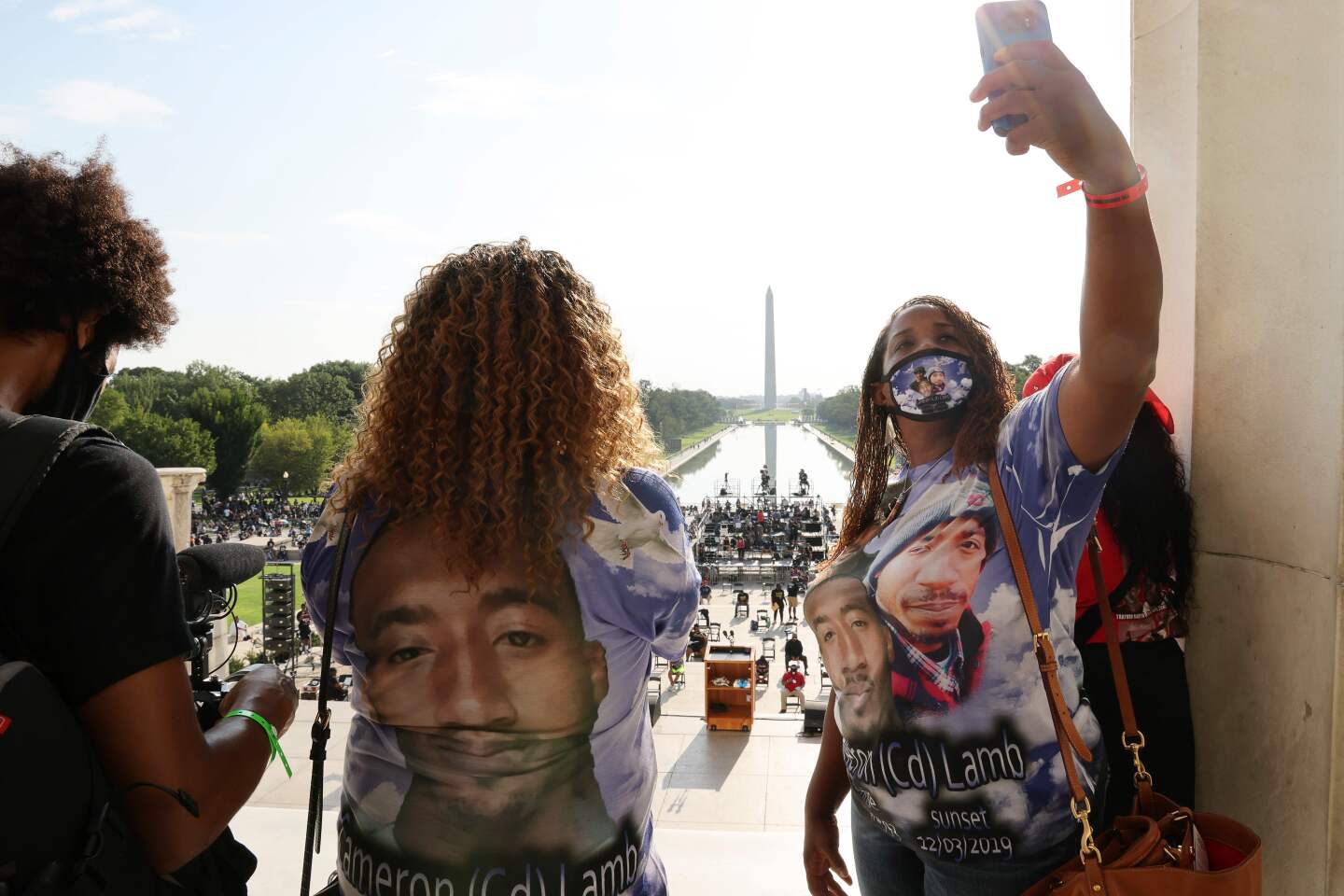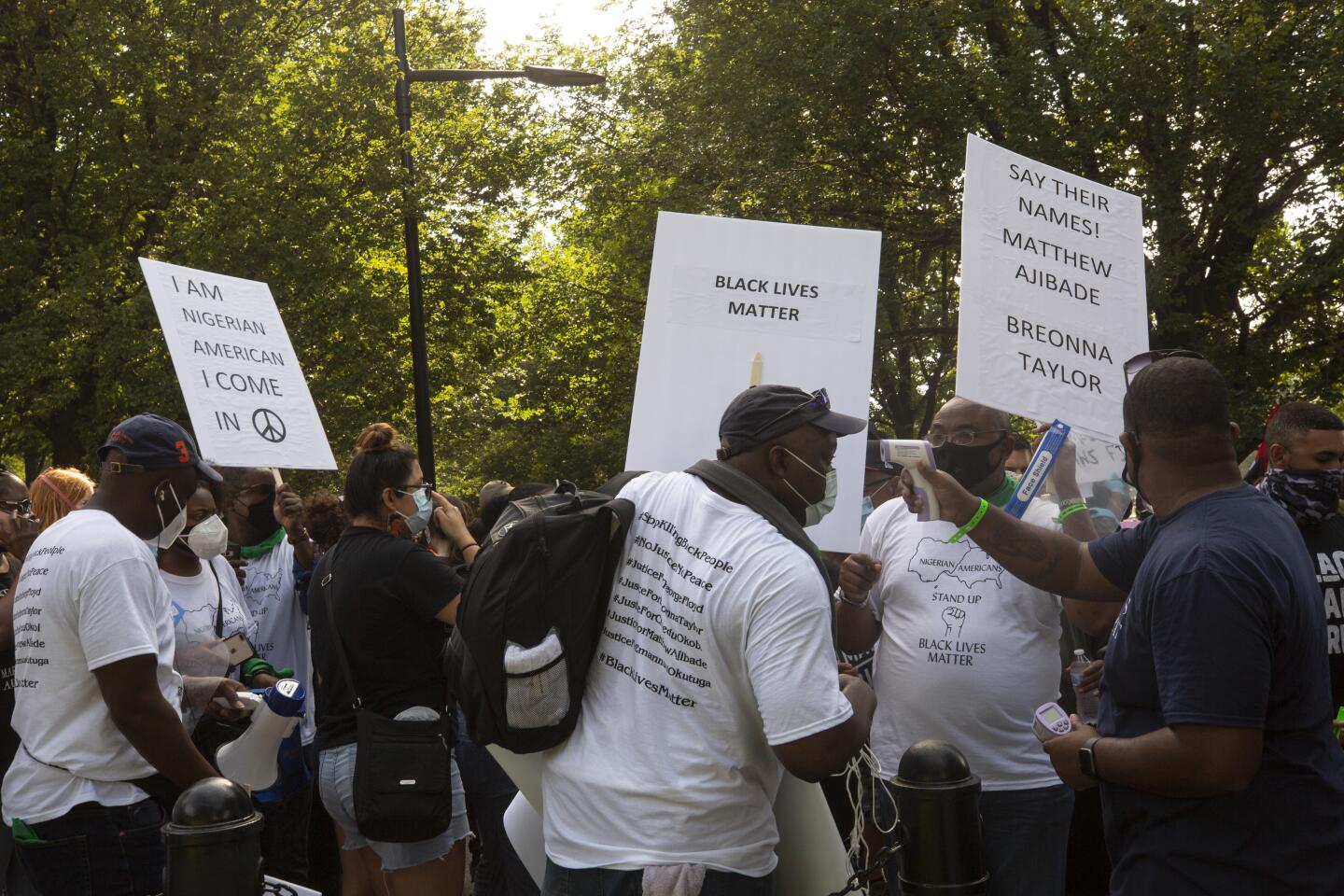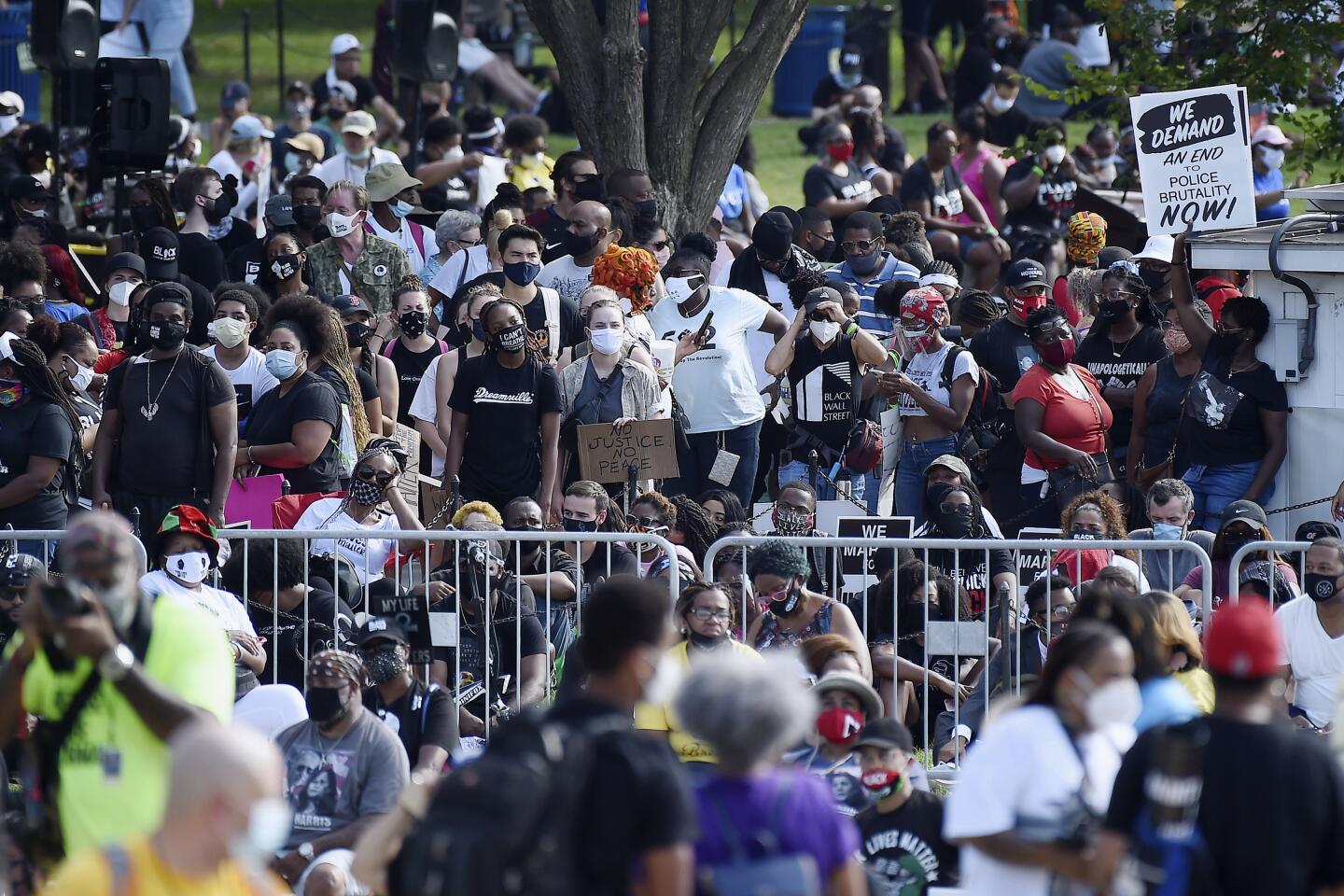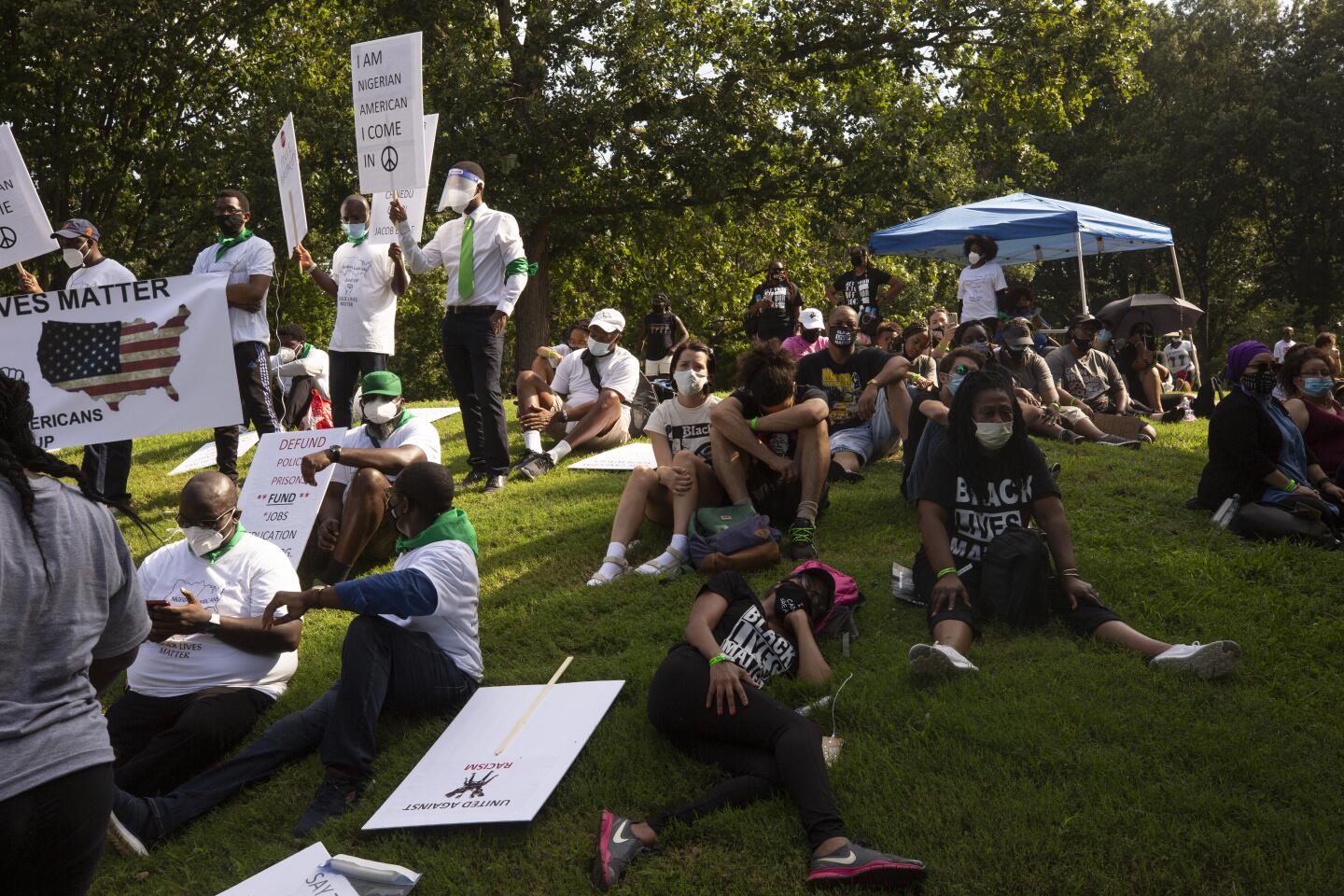Thousands gather for March on Washington commemorations
- Share via
WASHINGTON — Capping a week of protests and outrage over the police shooting of Jacob Blake in Kenosha, Wis., civil rights advocates on Friday denounced police and vigilante violence against Black Americans at a commemoration of the 1963 March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom.
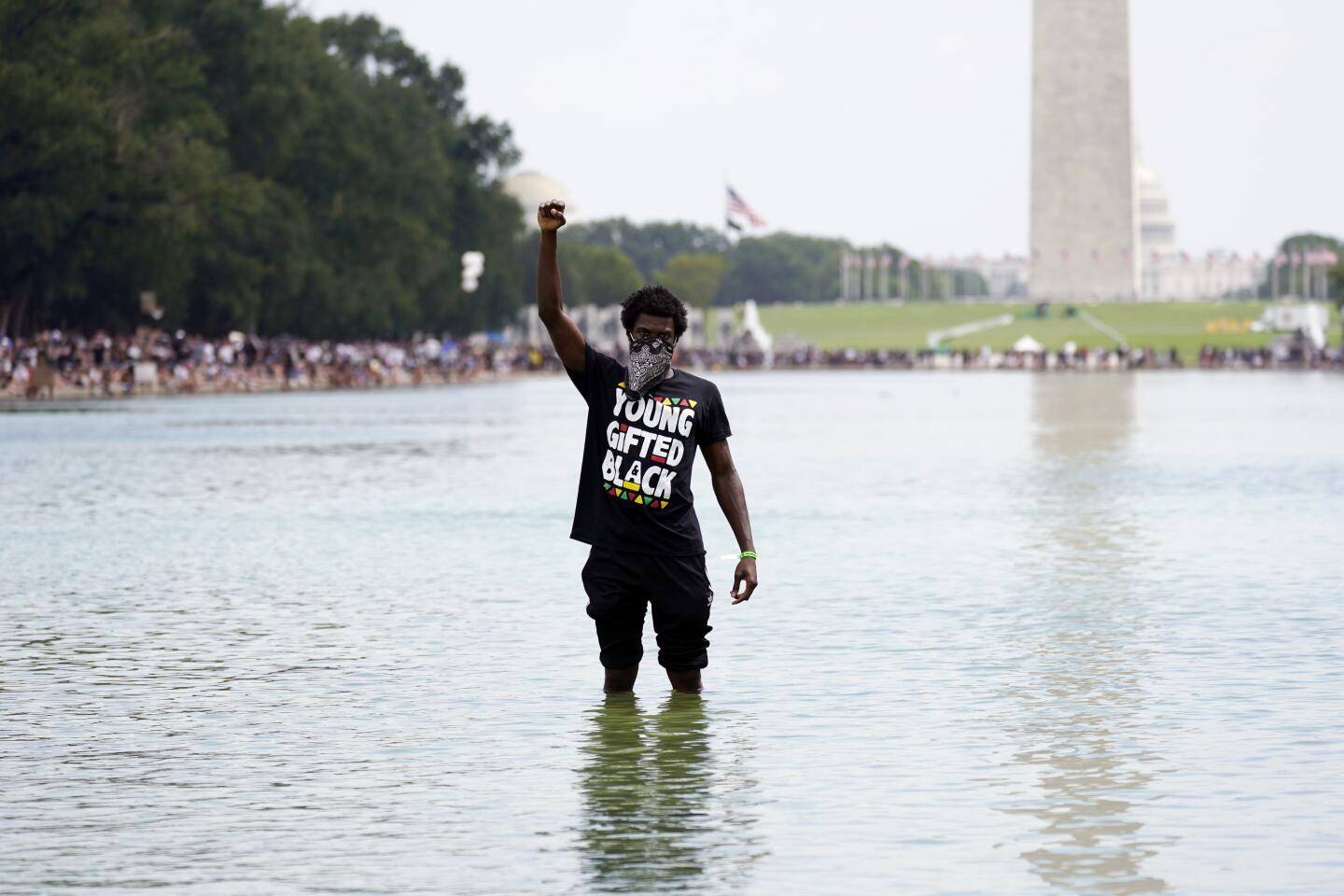
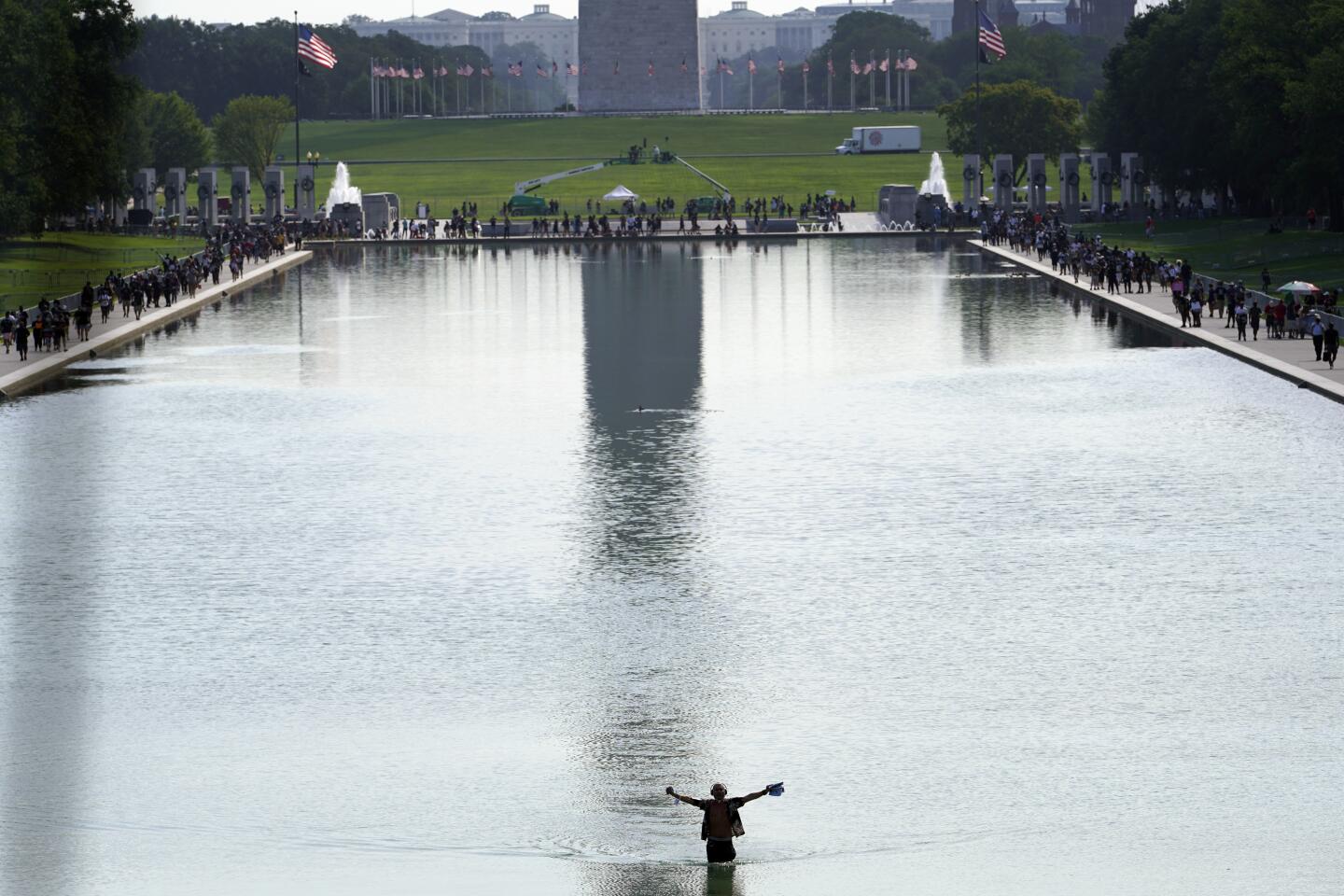
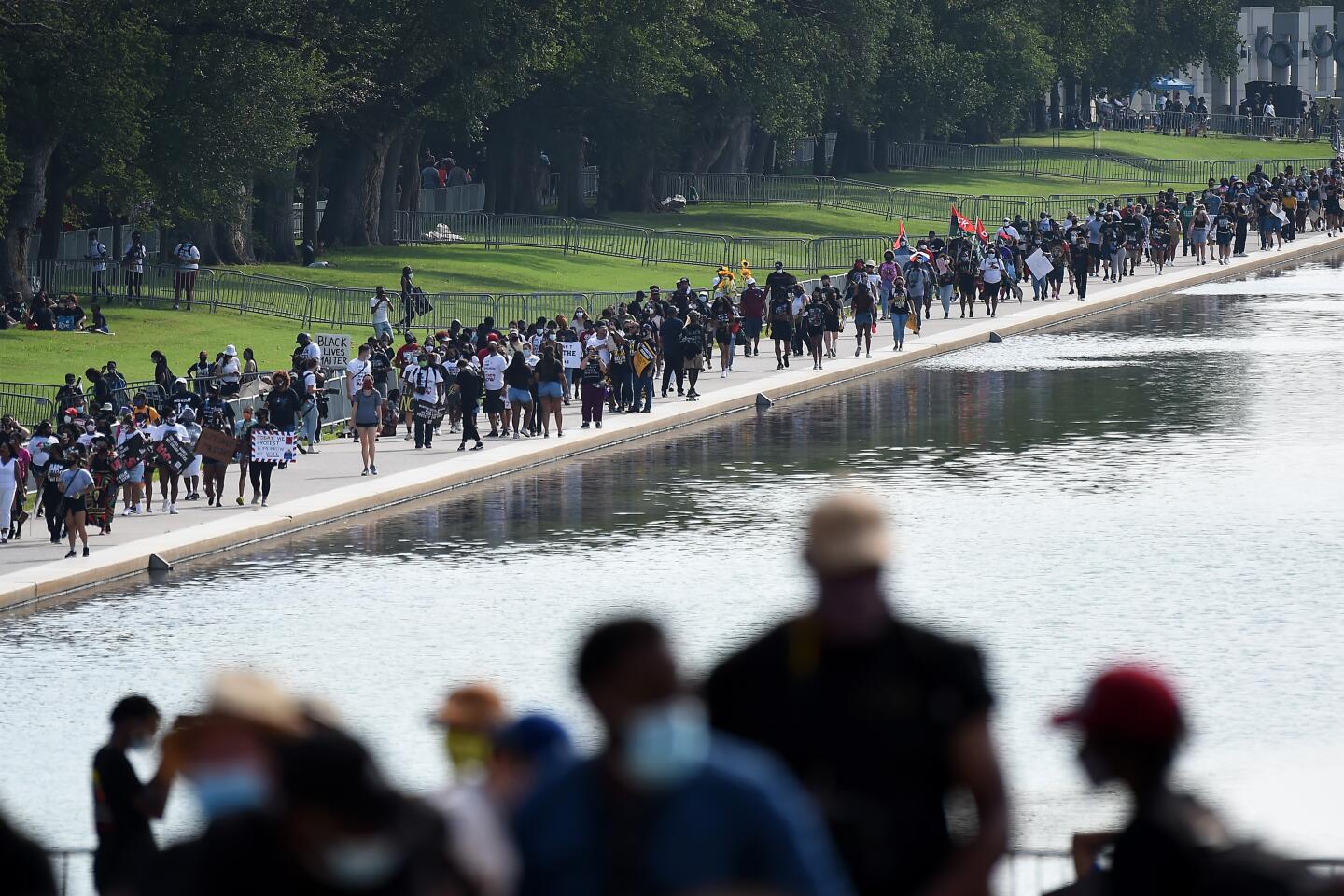
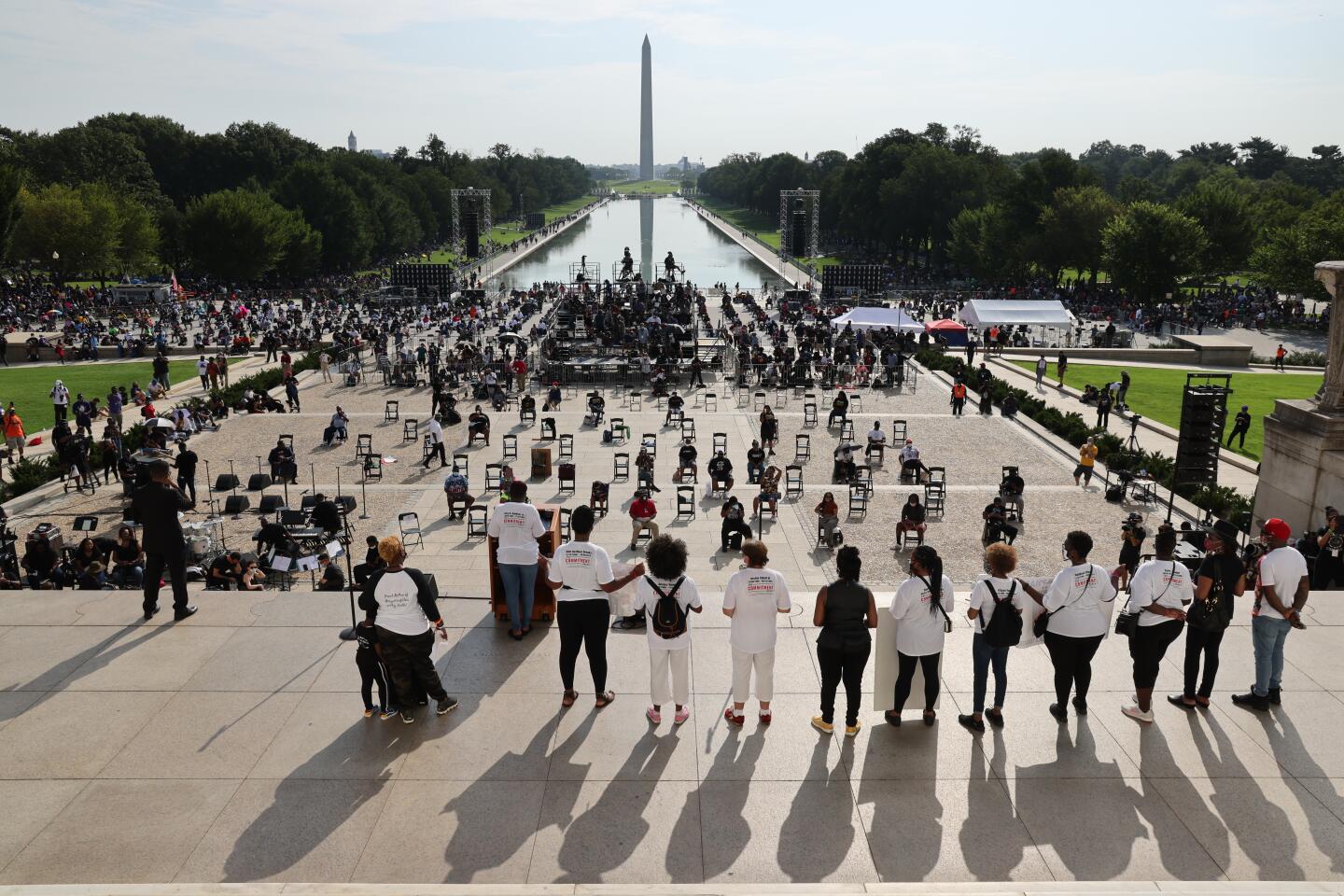
Thousands gathered near the steps of the Lincoln Memorial, where the Rev. Martin Luther King Jr. delivered his historic “I Have a Dream” address, a vision of racial equality that remains elusive for millions of Americans.
The event came on the heels of yet another shooting by a white police officer of a Black man — the 29-year-old Blake — that sparked days of protests and violence that left two dead.
“I want to give space for Black people in the crowd to say they are not OK,” said Jumaane Williams, New York City’s public advocate, who addressed march attendees shortly after the program began.
“We are like the nameless grandmothers who got in the streets and said ‘We will make you live up to what America says she is,’” Williams said. “We are here. We’re not going anywhere.”
Activist Frank Nitty, who said he walked 750 miles for 24 days from Milwaukee to Washington for Friday’s march, spoke to the audience about persistence in the fight for justice.
“Are y’all tired? Because I’m tired,” Nitty said. “They think this is a negotiation, but I came here to demand change. My grandson ain’t gonna march for the same things that my granddaddy marched for. This is a revolution.”
March attendee Jerome Butler, 33, of the District of Columbia, echoed Nitty’s sentiment.
“My hope is that my son doesn’t have to be out here in another 50 years protesting the same thing,” Butler said.
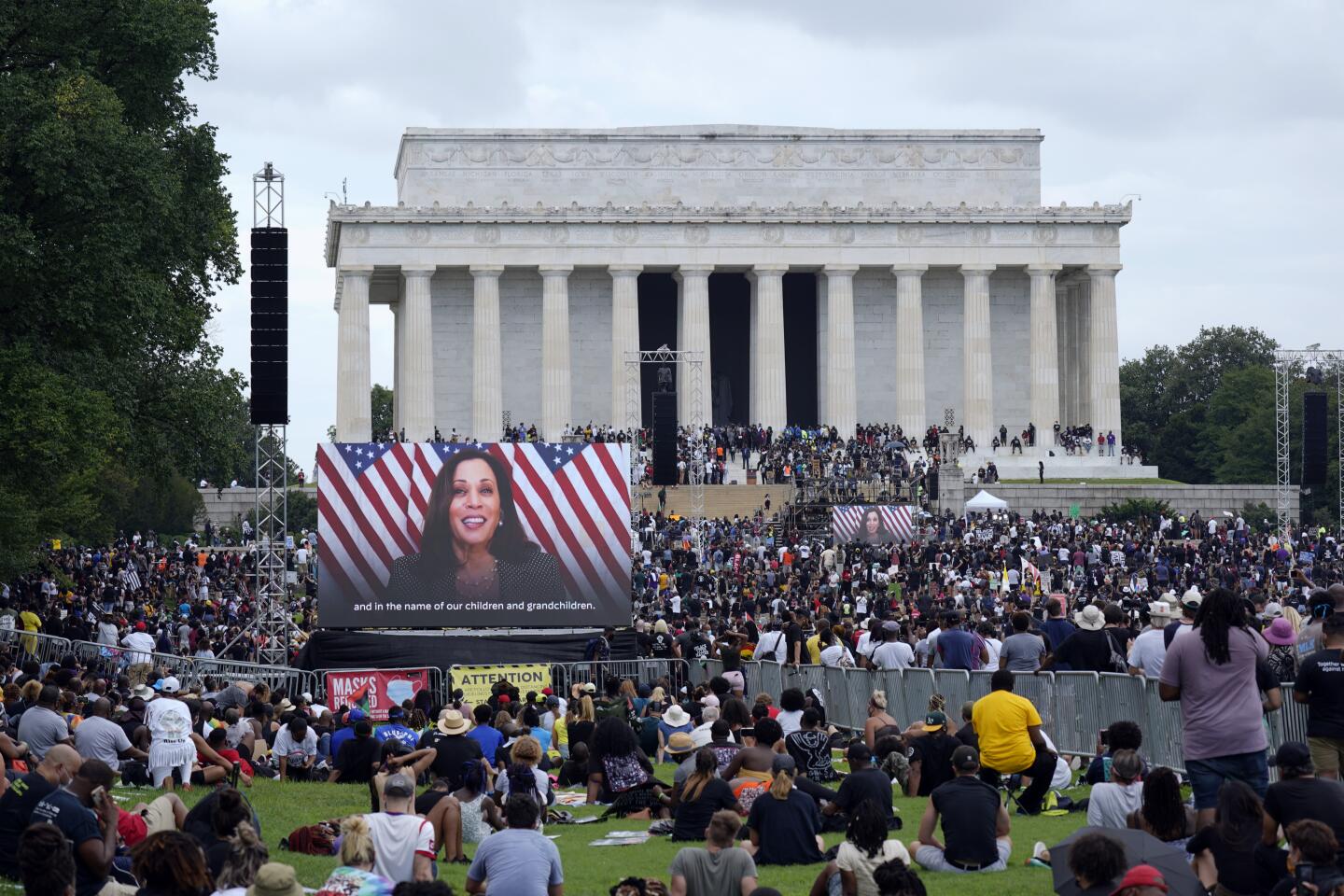
Early on, the march was shaping up to be the largest political gathering in Washington since the COVID-19 pandemic began. Many attendees showed up wearing T-shirts bearing the image and words of the late Rep. John Lewis who, until his death last month, was the last living speaker at the original March on Washington. That march is one of the most famous political rallies in U.S. history and one of the largest gatherings at the nation’s capital with more than 200,000 people advocating for social change.
Participants streaming in for the march late Friday morning stood in lines that stretched for several blocks, as organizers insisted on taking temperatures as part of coronavirus protocols. Organizers reminded attendees to practice social distancing and to wear masks throughout the program.
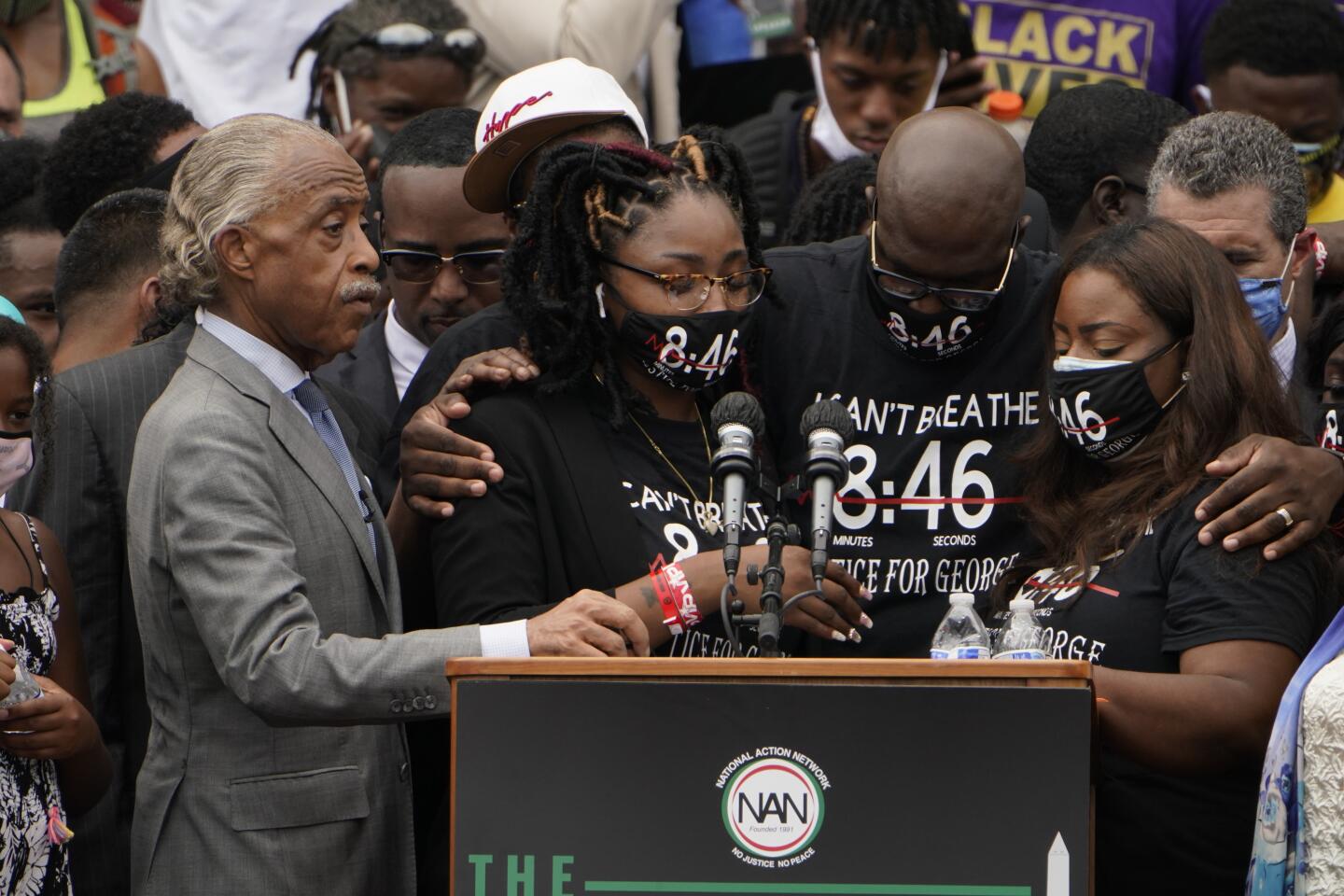
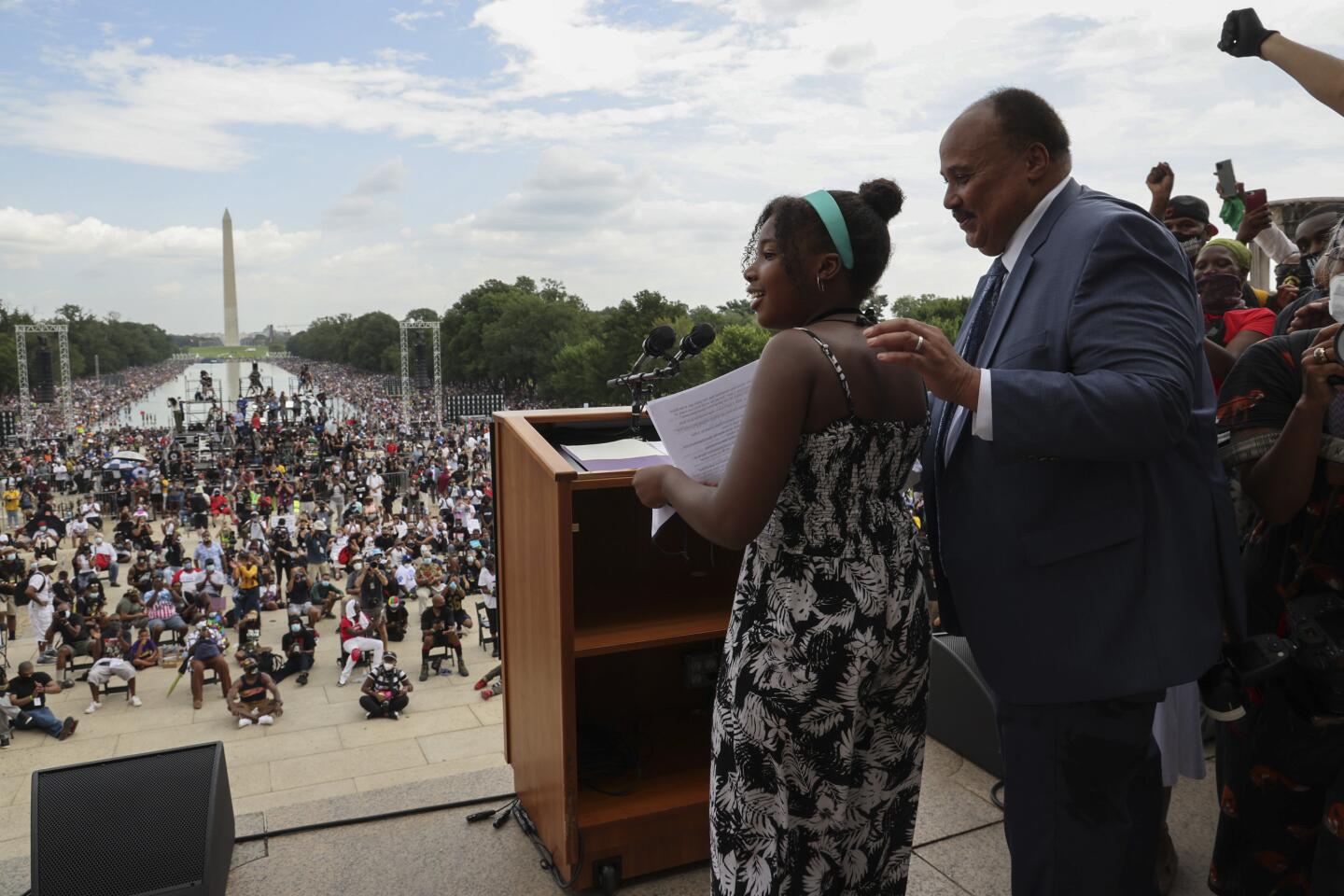
Martin Luther King III, a son of the late civil rights icon, and the Rev. Al Sharpton, whose civil rights organization, the National Action Network, planned Friday’s event, delivered keynote addresses that show the urgency for federal policing reforms, decry racial violence and demand voting rights protections ahead of the November general election.
“We’ve come to bear witness, to remain awake, to remember from where we’ve come and to carefully consider where we’re going,” King said. “Whether you’re here in person or watching on [television], thank you for joining us for this March on Washington.”
“We’re taking a step forward on America’s rocky but righteous journey toward justice,” he added.
“We didn’t just come out here to have a show,” Sharpton said. “Demonstration without legislation will not lead to change.”
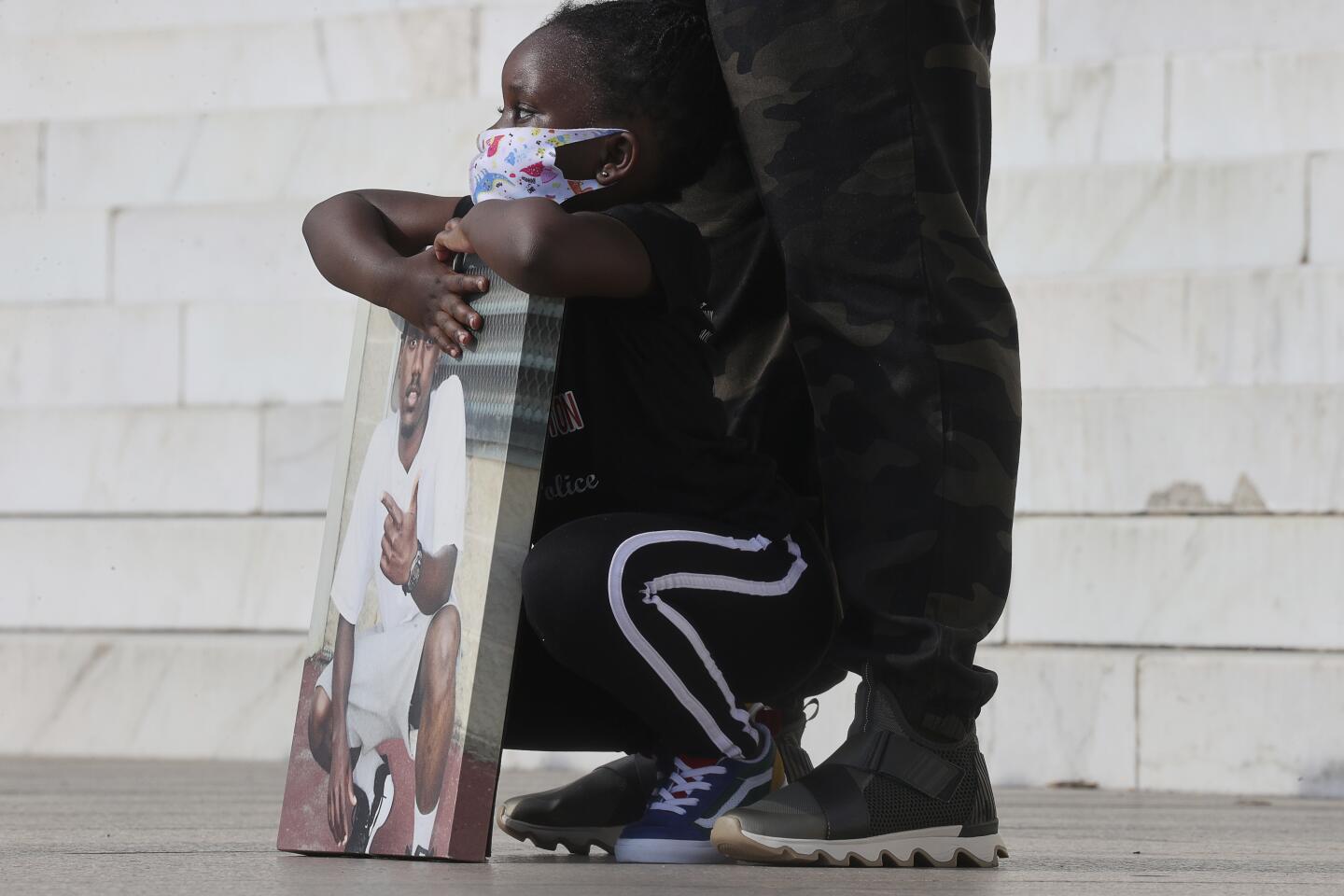
To underscore the urgency, Sharpton assembled the families of an ever-expanding roll call of Black people who died in encounters with police, including George Floyd, Breonna Taylor, Rayshard Brooks, Eric Garner and Blake.
Following the rally, participants were to march to the Martin Luther King Jr. Memorial next to the National Mall and then disperse.
Turnout in Washington was expected to be lighter than initially envisioned due to city-imposed pandemic restrictions that limit out-of-state visitors to the nation’s capital. As alternatives, the National Action Network organized a handful of satellite events in South Carolina, Florida and Nevada, among other locations.
Robbie Williams, 67, traveled to the march from Covington, Ky., and said attending was her way of “speaking to my children and my people.”
“My message to my children is to stand up no matter what. And to the police: Get some education and read your Bibles,” Williams said, adding that she also wants Black communities to honestly confront internal violence and homophobia.
Representation of Black lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and gender-nonconforming people in the movement was addressed by several march speakers, including David Johns, executive director of the National Black Justice Coalition, a Black LGBTQ civil rights organization.
“I stand here in the spirit of our brother Bayard Rustin,” he said, referring to the King advisor who helped organize the original march. “Without his brilliance and his commitment to our intersectional social justice, there would not have been a March on Washington.”
“If you care about Black people like I do, if you love Black people like I do, you’ve got to love and care about all of us,” Johns said.
While participants marched in Washington, Sharpton called for those in other states to march on their U.S. senators’ offices and demand their support of federal policing reforms. Sharpton said protesters should also demand reinvigorated U.S. voter protections, in Lewis’ memory.
In June, the Democrat-controlled House of Representatives passed the George Floyd Justice in Policing Act, which would ban police use of stranglehold maneuvers and end qualified immunity for officers, among other reforms. Floyd died May 25 after a white police officer in Minneapolis held a knee to his neck for about eight minutes, sparking weeks of sustained protests and unrest from coast to coast.
This once industrial and union town, like much of America, is facing a reckoning after the police shooting of Jacob Blake.
In July, following Lewis’ death, Democratic senators reintroduced legislation that would restore a provision of the historic Voting Rights Act of 1965 gutted by the U.S. Supreme Court in 2013. The law previously required states with a history of voter suppression to seek federal clearance before changing voting regulations.
Both measures are awaiting action in the Republican-controlled Senate.
Rep. John Lewis spent his whole life fighting for civil rights — and he wanted to make sure the cause lived on after his death.
In her remarks at the march, Rep. Sheila Jackson Lee, whose Texas district includes Floyd’s hometown of Houston, referenced a line from the “I Have a Dream” address in which King chides America for giving Black people “a bad check, a check which has come back marked ‘insufficient funds.’”
“Today, we stop the insufficient funds and we put money in the bank,” Lee said, vowing to keep pushing for enactment of the federal legislation.
Later in the evening, the Movement for Black Lives, a coalition of more than 150 Black-led organizations that make up the broader Black Lives Matter movement, will hold its virtual Black National Convention.
The convention will coincide with the unveiling of a new Black political agenda intended to build on this summer’s protests. The platform will deepen calls for defunding police departments in favor of investments to healthcare, education, housing and other social services in Black communities, organizers said.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.