Must Reads: The Navy’s newest destroyer, the Michael Monsoor, is as much an experiment as a ship-killer
- Share via
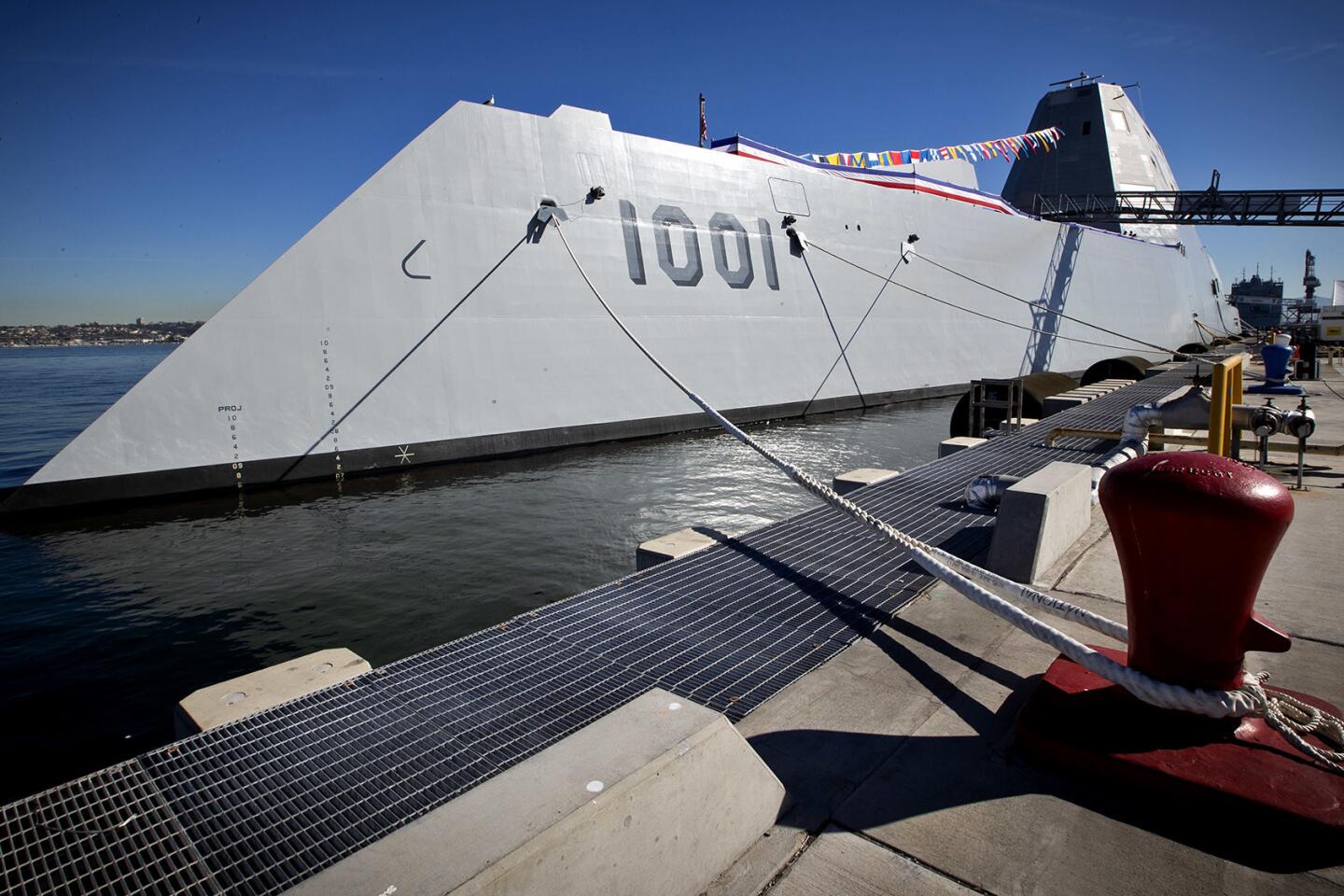
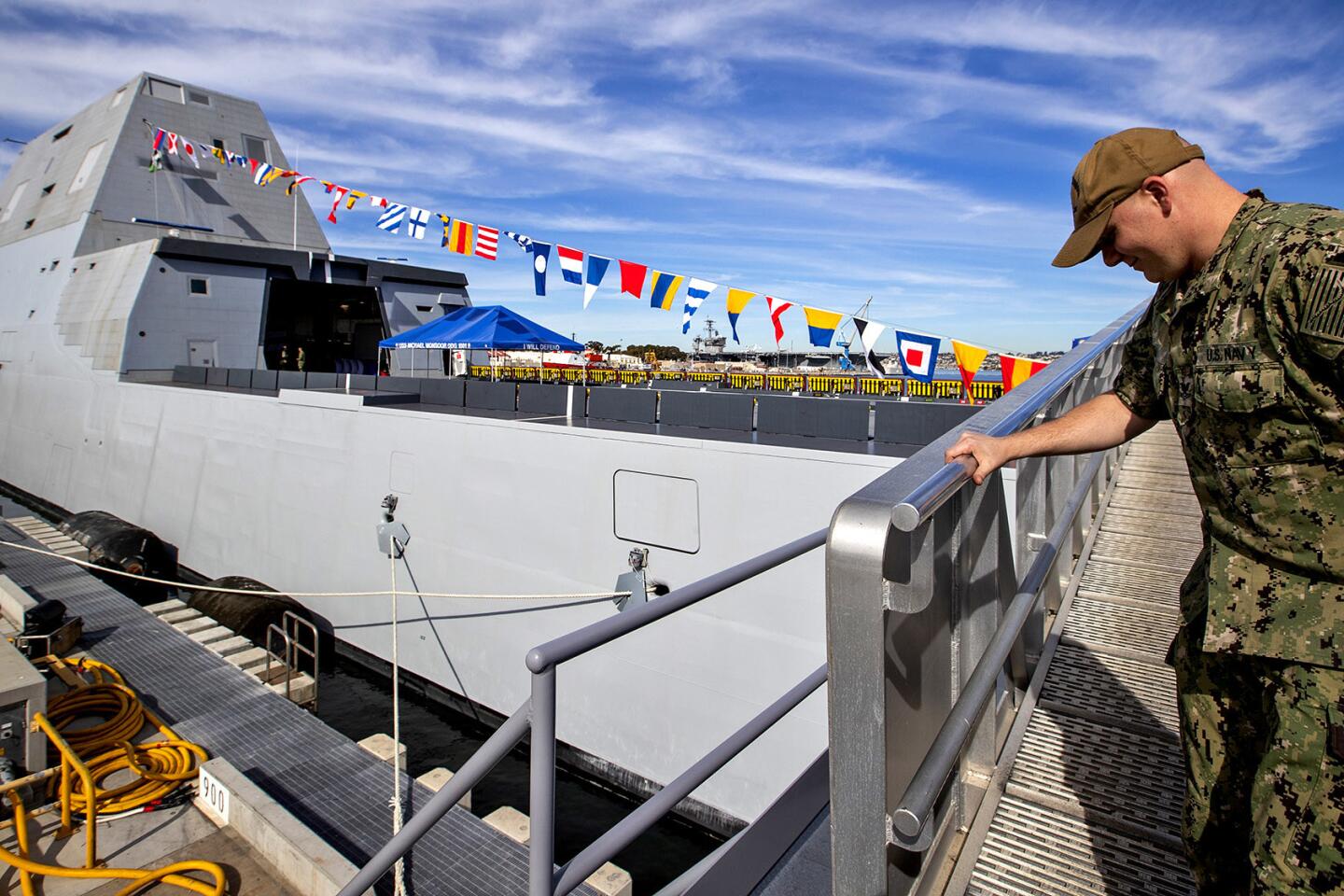
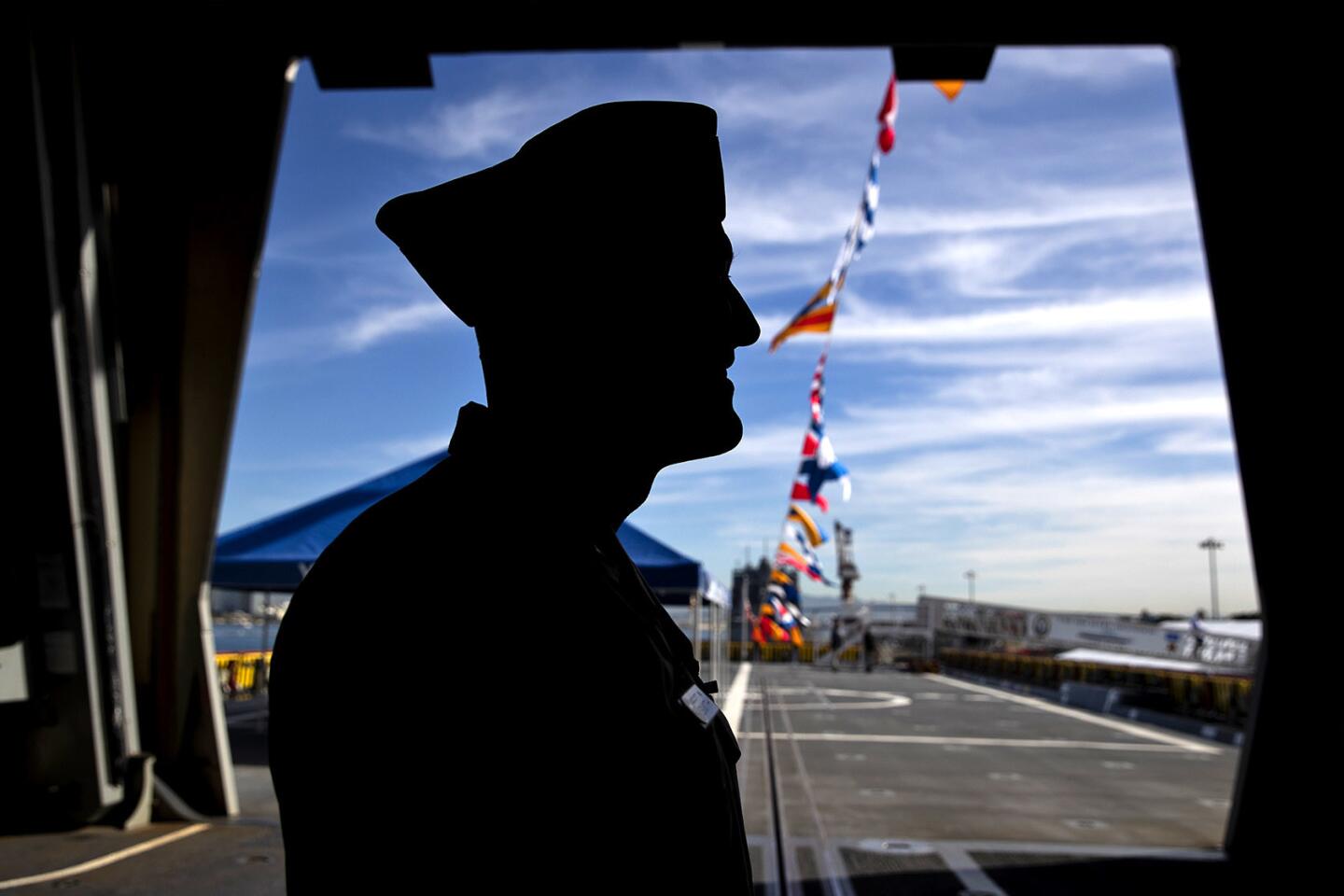
Reporting from San Diego — With slick sides and sharp angles, the Michael Monsoor and its sister ship Zumwalt cut a distinct silhouette along the waters of San Diego.
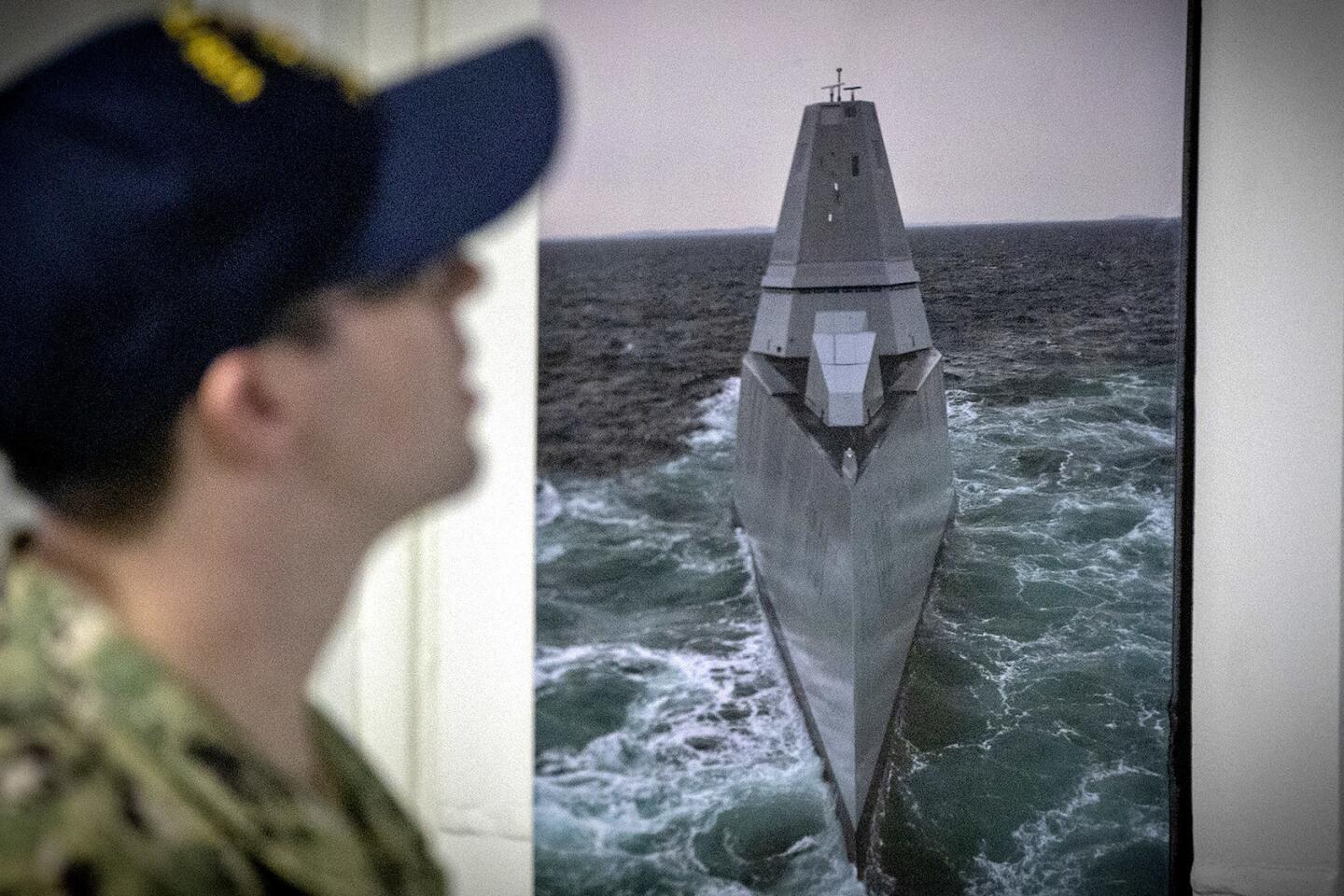
Unlike a nearby aircraft carrier whose radar juts into the air, the Monsoor’s composite material deckhouse is polygonal and covered with material that can absorb radar waves and increase the destroyer’s stealthiness. Its “tumblehome” hull looks like something you’d see on a ship built before World War I.
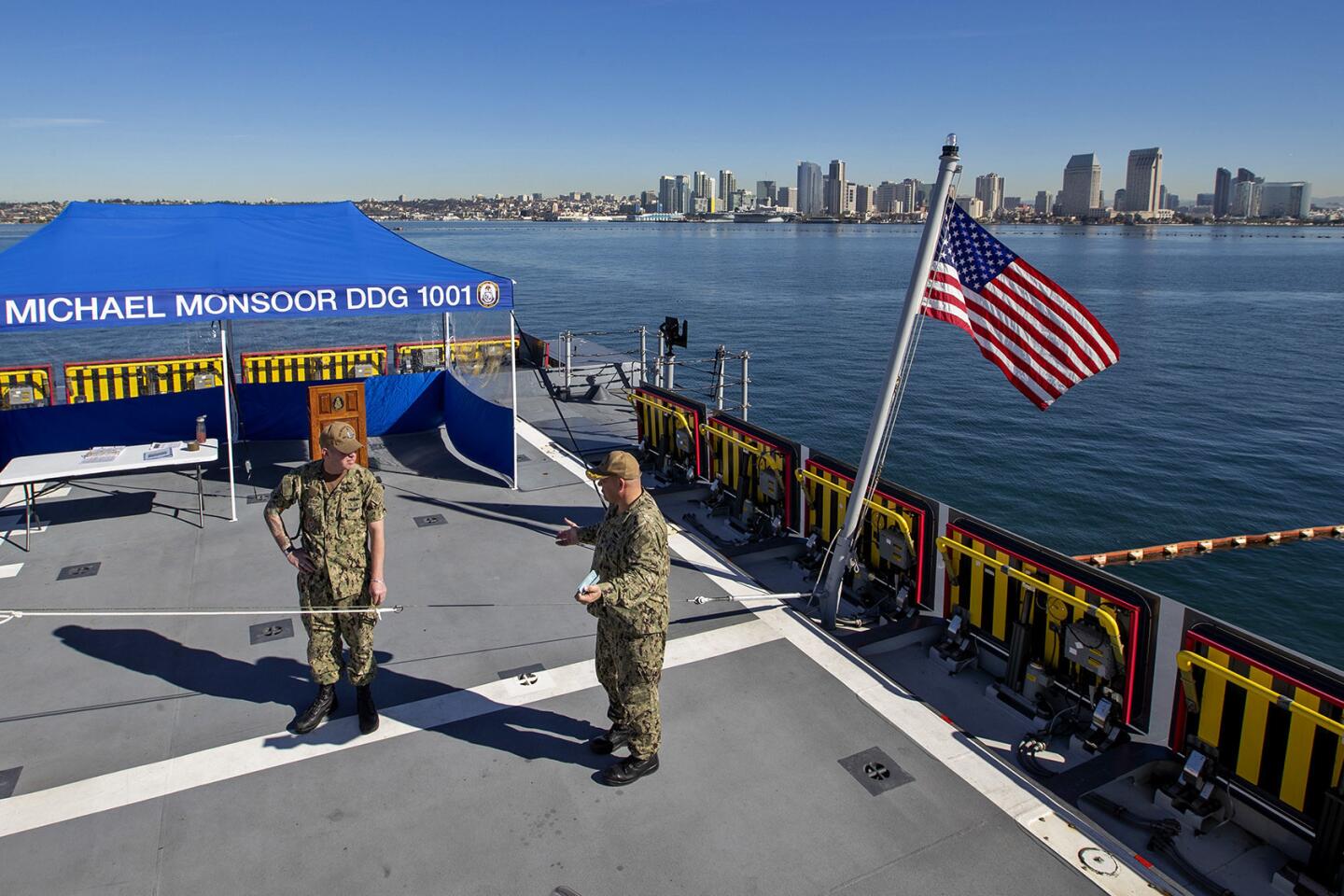
Make no mistake, the Monsoor guided-missile destroyer — named after Navy SEAL Michael A. Monsoor, who grew up in Garden Grove and died in 2006 saving the lives of three other SEALS — is one of the U.S. Navy’s most technologically advanced ships. It was commissioned Saturday in San Diego.
But developing that cutting-edge technology has proved more difficult than expected, and its deployment has been complicated by a strategic pivot in the ship’s mission.
In the end, what was once intended to be a class of 32 destroyers will now be only three — making for a per-ship cost of about $4.4 billion, according to a December 2016 estimate by the Government Accountability Office, the most recent cost estimate available. Including development costs, that number balloons to $8.2 billion, the GAO said.
The first two ships have been commissioned and are going through combat trials, while the third and final ship, the Lyndon B. Johnson, is scheduled for christening in late April.
“It’s got this size and weight and payload capacity, and because it has a lot of power capacity, it does bring to the fleet the ability to bring other weapons” online, said Bryan Clark, senior fellow at the Center for Strategic and Budgetary Assessments think tank. But, he said, “fleet design for the future has to think about [whether] they can introduce these technologies at sufficient capacity that they can be affordable and have enough of them to be operationally relevant.”
The Navy had planned to use the Zumwalt-class destroyers as a replacement for its aging Arleigh Burke-class destroyers, the first of which entered service in 1991. The idea was to use the Zumwalt ships in near-shore waters to support ground troops — a mission that reflected the anticipation of fights against land and sea forces from countries such as North Korea or Iran, according to an October Congressional Research Service report.
Instead, the Navy now finds itself refocused on planning for a more traditional mission: challenging the blue-water navies of competitors such as China and Russia. For that reason, as well as issues with the ships’ advanced gun system, the Zumwalt destroyers last year were rebranded as ship-killers, packing surface-to-surface cruise missiles.
The technology on the Zumwalt-class destroyers has been touted since the program began in the early 1990s.
The 15,000-ton ships’ use of automation means their crew is smaller — the Monsoor will have fewer than 150 sailors compared with the 300 or so needed on other destroyers or cruisers.
The advanced gun system on its deck was envisioned as a way to provide precision fire against land targets. The gun’s shells were to be rocket-propelled, guided by GPS and loaded by simply pressing a button.
The ship generates a massive amount of power — about 78 megawatts, enough to power a small city, the Navy says — to feed its propulsion system, while leaving plenty in reserve for future uses, said Capt. Scott Smith, commanding officer of the Monsoor, during a recent weekday tour of the ship. Those could include weapons currently in development, such as lasers.
The goal of a reduced radar, acoustic and infrared profile required some radical changes in design. Monsoor’s bridge has more than a dozen windows, but 360-degree visibility is provided via a handful of monitors that show images from around the ship. The tactical hub, known as the ship’s mission center, rivals a sports bar with its big-screen TVs.
The ship’s bow slopes forward, rather than backward, a design intended to give the destroyer better stability when launching weapons, Smith said. The hull’s design allows the destroyer to slice through waves, which is intended to generate less noise in the water and make for a smoother ride, some of its sailors say.
The Monsoor was designed to have no exterior accessories that would reflect radar. Much of the equipment on board is mounted in such a way that it will not touch the ground and vibrations won’t reverberate throughout the ship and into the water.
“Where you would normally have people out on the decks underway or the occasional cigar out on the bridge wing, those days sadly are gone,” Smith said with a laugh.
In July 2008, after the first two Zumwalt-class destroyers had already been procured, the Navy said it wanted to stop ordering new Zumwalts and instead continue buying less-costly Arleigh Burke destroyers.
That reflects the service’s shift to prepare for “great power competition,” involving sophisticated naval forces from competitors such as Russia and China, according to the Congressional Research Service report.
Now ships would have to counter submarine attacks and anti-ship cruise missiles, but also would play a role in warding off ballistic missiles. The Navy concluded the Arleigh Burke destroyers could “perform these three missions adequately and would be less expensive to procure,” according to the report.
At the same time, the Zumwalt ships were facing schedule pressures and technological hurdles. Written testimony from a GAO official before a House subcommittee in 2008 highlighted lagging demonstrations of the ships’ power system, as well as development delays with one of the ships’ dual-band radar system.
Last year, one of the Monsoor’s engines was found to be damaged, resulting in the removal of that entire engine from the ship. The ship’s two MT30 marine gas turbines are based on the aircraft engine that powers the Boeing 777 commercial airplane and can be powered by JP-5 jet fuel.
Today, much of the Monsoor’s radar system has already been installed, though testing isn’t yet complete.
With the reduced number of ships in the class, the cost of the gun system’s rocket-guided shells also jumped to at least $800,000 apiece, which analysts said contributed to the change in the destroyers’ mission. The Navy chose to cancel purchase of those munitions, and new ammo for the guns has yet to be determined, though the service is “actively looking” for other rounds, Smith said. One possibility — a “hyper-velocity” guided round that could accelerate to Mach 3 — was tested on a Navy destroyer last year, according to U.S. Naval Institute News.
So for now, the Zumwalt ships have guns but nothing to shoot from them.
In a November hearing of the Senate Armed Services Subcommittee on Seapower, Vice Adm. William Merz, deputy chief of naval operations for warfare systems, said the Navy determined that the “best future” for the Zumwalt was to “get it out there with the capability it has, and separate out the advanced gun system, leaving everything else in place.”
He described it as a “very capable platform, with or without that gun,” and said the ship would likely be a candidate for any advanced weapons system that was developed.
“The fleet design of the future needs to yield both capacity and capability — not just capability,” said Clark of CSBA.
It’s not uncommon for follow-on ships in a cutting-edge class to benefit from lessons learned, said Shelby Oakley, a director of the GAO who leads reviews of Navy shipbuilding acquisitions. “There’s a natural build-up of knowledge from one ship to the next,” she said.
Smith said that’s already happening on the Monsoor. When the lead ship in the class, the Zumwalt, had issues with its radiator, the program office changed the water flow rates, which prevented the Monsoor from having the same problems, he said.
“Just as they gave us a baseline of information, we have been taking that and tried to refine that,” he said. “We’ll just keep swapping off back and forth and growing together.”
Analysts said the Zumwalt-class destroyers will likely be used in the future as platforms to introduce new technology because of their extra payload and power capability. Smith compared the Zumwalt-class destroyers to the Seawolf-class nuclear-powered attack submarines, the first of which was commissioned in 1997.
Like the Zumwalt ships, only three Seawolf submarines were produced. But they influenced the smaller, less expensive Virginia-class submarines that followed, which Smith described as “one of the most successful submarine programs.”
“It’s that leading edge,” Smith said. “Everything that follows will be impacted by what we’re doing.”
Twitter: @smasunaga
More to Read
Inside the business of entertainment
The Wide Shot brings you news, analysis and insights on everything from streaming wars to production — and what it all means for the future.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.