Editorial: A welcome assault on the gender wage gap
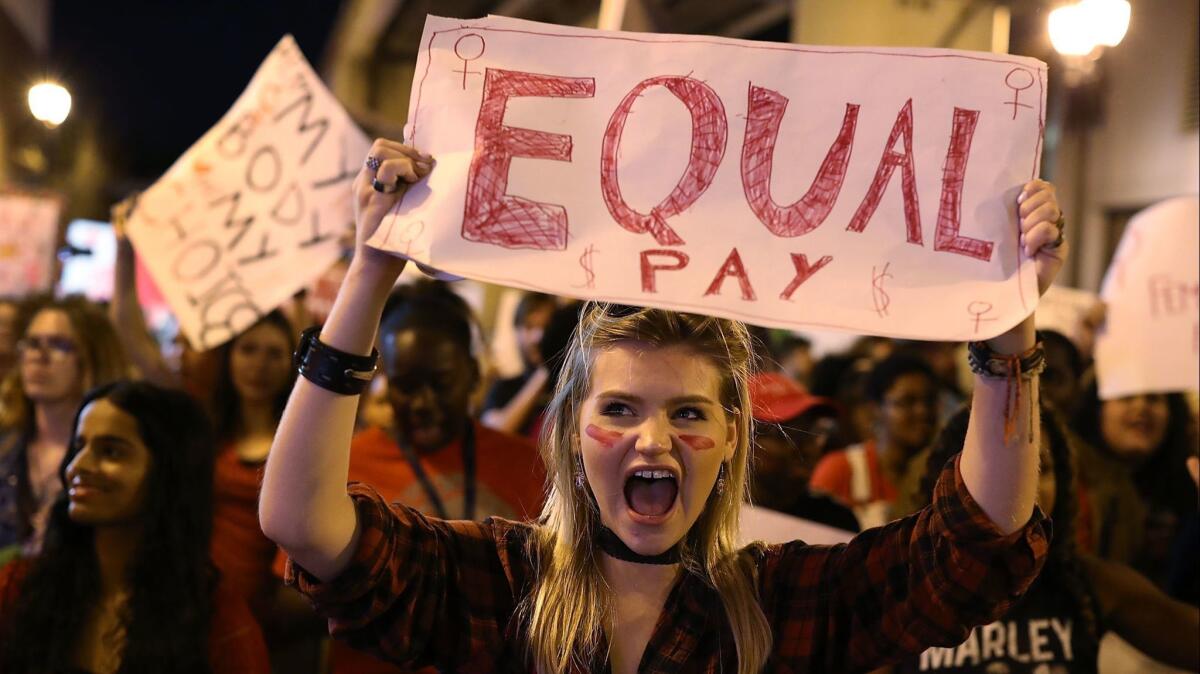
- Share via
Year after year, study after study has come to the same depressing conclusion: Women are paid less than men in most every occupation, from accounting to teaching to sales to nursing. In the 55 years since the federal Equal Pay Act was passed, the gap has shrunk a bit, but it’s still far too wide. In 1963, working women were paid, on average, 59 cents for every dollar paid to a man. It’s now about 80 cents on the dollar, and substantially less for women of color. The gap exists even in fields in which women vastly outnumber men, like secretarial work and grade school teaching.
It’s no great mystery how and why this gap came to exist, but it is unfair and dispiriting nonetheless. Well into the technologically enlightened 21st century, some prehistoric attitudes about the value of women’s work persist and are reflected in their collective pay. It’s wrong, but deeply held societal beliefs are hard to shake and structural inequities are difficult to rectify. That’s why we are heartened by the disruptive promise of a recent decision by the U.S. 9th Circuit Court of Appeals that bars employers from considering a new worker’s prior salary when deciding what to pay him or her.
Well into the technologically enlightened 21st century, some prehistoric attitudes about the value of women’s work persist and are reflected in their pay.
The ruling came in the case of a California woman who sued the Fresno County Office of Education when she found out her salary was $13,000 less than that of a man with less experience and education hired for the same job. Her employers argued that the disparity was not discriminatory because her lower salary was based on the fact that she had earned less in her last job, not on her gender. The court disagreed, adding (in an opinion written by Judge Stephen Reinhardt, who died in late March) that “to allow employers to capitalize on the persistence of the wage gap and perpetuate that gap ad infinitum — would be contrary to the text and history of the Equal Pay Act, and would vitiate the very purpose for which the Act stands.”
It’s a broad interpretation, to be sure. Even some of the concurring justices worried that Reinhardt’s absolute ban on considering prior salary was too broad, though they agreed with his larger point. But there’s certainly something to his logic. Discrimination is baked deeply into our system, and because past pay often is determinative of future pay, women underpaid in the past often continue to be paid less for the rest of their careers. Interrupt this pattern, and you have a better chance of stopping it before another century passes.
The ruling applies only to the nine states under the appeals court’s jurisdiction, but it likely will have a ripple effect across the nation, where concerns about the wage gap already have spurred a handful of states and cities — California among them — to adopt laws banning employers from asking about pay history. More states have considered similar proposals.
Businesses that employ people have been understandably wary of adding another subject to the list of topics that are verboten to ask about in the application process. This includes asking job applicants their race, religion or gender identity, or other personal information such as their sex or whether they are pregnant, unless is it relevant to the job they are seeking. The California Chamber of Commerce and other business groups opposed California’s law, AB 168, which went into effect in January, on the grounds that employers often seek past wage history for legitimate, nondiscriminatory purposes. For one thing, the chamber argued, employers don’t always know what the going market salary is for a particular job; for another, past wage history can help a company determine whether the potential employee’s salary expectations far exceed what it can offer.
But the benefits of the law outweigh those concerns. Besides, industry trade groups regularly produce salary surveys for employers in their fields. And the California law still allows employers to ask an applicant about their salary expectations — what they hope or expect to earn in the job for which they’re applying.
Pay inequity doesn’t only harm women. It also harms people of color. And it’s a matter of simple fairness too. Two people with the same amount of job experience and the same skills who do the same job equally well should be paid roughly the same amount, regardless of what they used to earn or what their race or gender is.
Everyone can be hurt by a system that bases compensation not on skill level, experience or industry standards but on what they were paid at their last job.
Follow the Opinion section on Twitter @latimesopinion and Facebook
More to Read
A cure for the common opinion
Get thought-provoking perspectives with our weekly newsletter.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.









