A welcome casualty, for once, of the COVID-19 pandemic: flu
- Share via
NEW YORK — February is usually the peak of flu season, with doctors’ offices and hospitals packed with suffering patients. But not this year.
Flu has virtually disappeared from the U.S., with reports coming in at far lower levels than anything seen in decades.
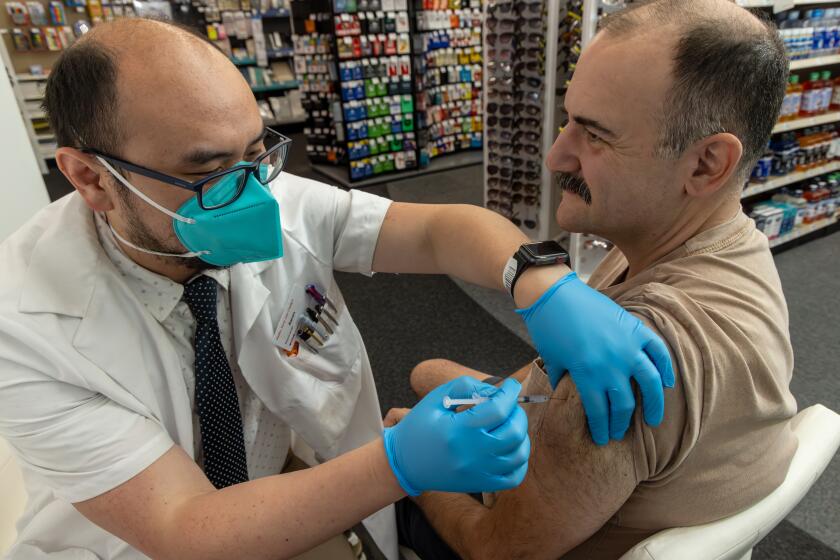
Experts say that measures put in place to fend off the coronavirus — mask-wearing, social distancing and virtual schooling — were a big factor in preventing a feared “twindemic” of flu and COVID-19. A push to get more people vaccinated against flu probably helped, too, as did fewer people traveling, they say.
Another possible explanation: The coronavirus has essentially muscled aside flu and other bugs that are more common in the fall and winter. Scientists don’t fully understand the mechanism behind that, but it would be consistent with patterns seen when certain flu strains predominate over others, said Dr. Arnold Monto, a flu expert at the University of Michigan.
Nationally, “this is the lowest flu season we’ve had on record,” according to a surveillance system that is about 25 years old, said Lynnette Brammer of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Hospitals say the usual steady stream of flu-stricken patients never materialized.
Winter is ending in the Southern Hemisphere and country after country had a surprise: Steps against COVID-19 also apparently helped blocked the flu.
At Maine Medical Center in Portland, the state’s largest hospital, “I have seen zero documented flu cases this winter,” said Dr. Nate Mick, the head of the emergency department.
Ditto in Oregon’s capital city, where the outpatient respiratory clinics affiliated with Salem Hospital have not seen any confirmed flu cases.
“It’s beautiful,” said the health system’s Dr. Michelle Rasmussen.
The numbers are astonishing considering that flu has long been the nation’s biggest infectious-disease threat. In recent years, it has been blamed for 600,000 to 800,000 annual hospitalizations and 50,000 to 60,000 deaths.
This southeastern Arizona town, once a tourist haven, is struggling during the coronavirus pandemic.
Across the globe, flu activity has been at very low levels in China, Europe and elsewhere in the Northern Hemisphere. And that follows reports of little flu in South Africa, Australia and other countries during the Southern Hemisphere’s winter months of May through August.
The story has, of course, been different with COVID-19, which has killed more than 500,000 people in the United States. Coronavirus cases and deaths reached new heights in December and January before beginning a recent decline.
Flu-related hospitalizations, however, are a small fraction of their normal level during even a very mild season, said Brammer, who oversees the CDC’s tracking of the virus.
Flu death data for the whole U.S. population are hard to compile quickly, but CDC officials keep a running count of deaths of children. One pediatric flu death has been reported so far this season, compared with 92 reported at the same point in last year’s flu season.
“Many parents will tell you that this year their kids have been as healthy as they’ve ever been, because they’re not swimming in the germ pool at school or daycare the same way they were in prior years,” Mick said.
Some doctors say they have even stopped sending specimens for testing, because they don’t think flu is present. Nevertheless, many labs are using a CDC-developed “multiplex test” that checks specimens for both the coronavirus and flu, Brammer said.
More than 190 million flu vaccine doses were distributed this season, but the number of infections is so low that it’s difficult for the CDC to make its annual calculation of how well the vaccine is working, Brammer said. There are simply not enough data, she said.
That also is challenging the planning of next season’s flu vaccine. Such work usually starts with checking which flu strains are circulating around the world and predicting which of them are likely to predominate in the year ahead.
“But there’s not a lot of [flu] viruses to look at,” Brammer said.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.