With ultra-contagious BA.5 rising, how close is L.A. to an indoor COVID mask mandate?

- Share via
Continued increases in coronavirus cases fueled by the ultra-contagious BA.5 subvariant as well as a rise in hospitalizations have pushed Los Angeles County even closer to reinstating a universal indoor mask mandate.
The measure, which officials have long warned was on the table, could go into effect as soon as late July.
“We can’t predict with certainty what the future hospitalization trend will look like. However, it is looking more likely, as cases and admissions have continued to increase, that we’ll enter the high community level designation later this month,” L.A. County Public Health Director Barbara Ferrer said Thursday.
Here is what you need to know:
L.A. County’s coronavirus case rate hit its highest point in nearly five months over the Fourth of July holiday weekend.
When could L.A. County issue a new mask mandate?
Officials have said a public indoor masking requirement would be reinstated should L.A. County reach the high COVID-19 community level, defined by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and remain there for two consecutive weeks.
L.A. County has not yet entered that level — the worst on the CDC’s three-tier scale. But it is the closest it has been since exiting from it in early March. The category indicates not only that a region is experiencing significant coronavirus spread but that transmission is starting to exert stress on hospitals.
The CDC updates its community level assessments every Thursday. Assuming L.A. County were to enter the high COVID-19 community level next week, on July 14, and remain there on July 21 and July 28, the soonest a mask mandate could be issued would likely have an effective date of July 29, according to Ferrer.
There’s no guarantee that will happen, though. Projections are based on the possibility of current trends continuing.
How close are we?
To reach the high community level, L.A. County would need to observe at least 10 new weekly coronavirus-positive hospitalizations for every 100,000 residents.
According to CDC data released Thursday, the rate listed for L.A. County was 9.7, a 17% increase from the previous week’s rate of 8.3.
However, from the county’s perspective, the actual figure is lower — 8.4.
That, Ferrer said, is because federal data combines L.A. and Orange counties, as the two fall within the same health service area that the CDC uses to calculate its metrics.
“This approach was not initially problematic, as the L.A. County and the Orange County metrics were relatively similar,” Ferrer said.
But that’s no longer the case. Ferrer said Orange County’s rate of new weekly coronavirus-positive hospitalizations for every 100,000 residents was 13.3 as of Wednesday.
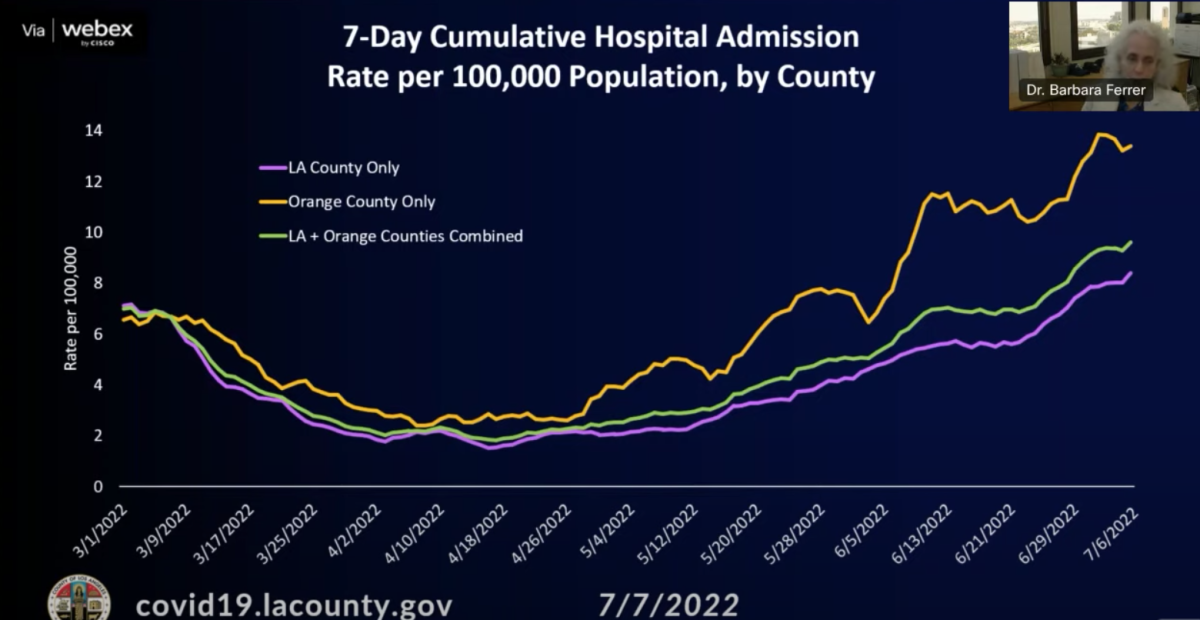
“Given this divergence, which now actually will affect the level assignment and designation, we’re going to use the L.A. County-specific data in determining the hospital metrics that are used to make the designated community level assignments,” she said.
Based on current trends, however, Ferrer estimated the L.A. County rate could surpass the high threshold as soon as next week.
Taking preventative measures is especially important now as BA.4 and especially BA.5 can reinfect even those who recently contracted an earlier Omicron subvariant.
Why is L.A. County considering a mask mandate?
Officials say the potential order is aligned with guidance from the CDC, which recommends indoor masking for counties in the high COVID-19 community level.
About 60% of California’s counties are in that category, including in the San Francisco Bay Area and Central Valley. Some 16 million Californians live in a county with a high COVID-19 community level, accounting for 41% of the state’s population.
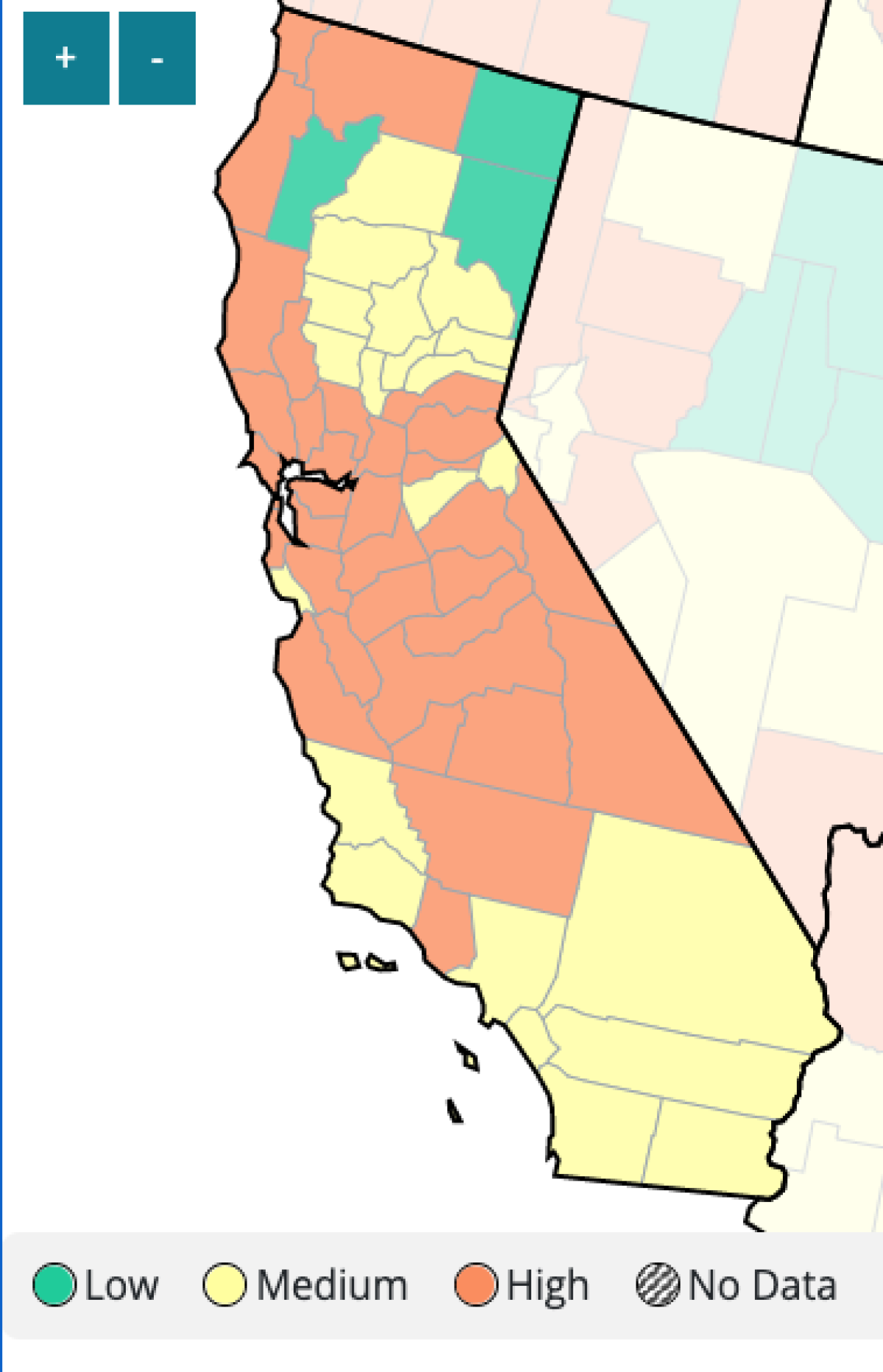
In Southern California, Ventura County is the only county in the high community level.
However, no other California counties have publicly linked the return of universal mask mandates to the CDC framework. And the only region to reissue a face covering order in response to the latest wave, Alameda County, has already rescinded it.
The coronavirus subvariants are not only especially contagious but also capable of reinfecting those who have survived earlier Omicron infection.
Though health officials almost universally recommend indoor masking as an extra layer of protection against coronavirus transmission, some have characterized new mandates at this time as unnecessary, given both epidemiological changes in the virus and the availability of vaccines and treatments.
Ferrer, though, says universal masking doesn’t just help protect the individual.
“While it’s true we have an amazing set of tools that we can all use to protect ourselves — and in fact, some of those tools will protect lots of other people as well — there are many people, particularly in essential work environments, where they would benefit if more people around them were actually using some of the safety precautions that we know work,” she said. “And that’s the case with masking.”
For L.A. County, she added, “equity issues are paramount.”
“Partly, we’re such a large jurisdiction; partly, we’ve witnessed really tragic and unconscionable differences and disproportionality in who’s been the hardest hit, that we want to make sure that where we have a simple and effective tool that can be used ... that we make sure that we’re using that tool when the risk level gets high,” she said.
There are reasons for health officials to be particularly cautious about the effects of a pandemic wave in L.A. County.
L.A. County is considered by the CDC as highly vulnerable in a pandemic, according to the agency’s Social Vulnerability Index, based on factors like poverty and crowded housing.
By contrast, its neighboring coastal counties — Ventura and Orange — as well as the five most populous counties in the San Francisco Bay Area — including Alameda County — have moderate levels of vulnerability.
In L.A. County, 14% of residents live below the poverty line; in Ventura County, 9% do.
L.A. County’s median household income of about $71,000 is below the state median of nearly $79,000, while Ventura County’s is higher, at $89,000.
There are two antiviral pills available for eligible patients who have recently tested positive for the coronavirus. And they’re free.
How are hospitals faring?
As of Thursday, 1,021 coronavirus-positive patients were hospitalized in L.A. County. That’s the highest single-day total since late February and a 38% increase from two weeks ago.
While the trendline has not yet taken the ominous, near-vertical shape seen during the worst waves of the pandemic, the daily patient count has more than quadrupled since mid-April.
“The worry, of course, with the increase in hospitalizations is that there may be more individuals at risk for severe illness that are getting infected now, given the highly transmissible new variants,” Ferrer said.
So far, though, this latest surge is not wreaking anywhere close to the same kind of havoc as those that came before. During the initial Omicron spike last fall and winter, coronavirus-positive hospitalizations topped out above 4,800. For last summer’s Delta surge, the peak was nearly 1,800.
During winter 2020, L.A. County’s coronavirus-positive patient count at times exceeded 8,000.
Since the hyper-transmissible Omicron variant appeared in early December, the coronavirus has affected nearly every family and social circle.
A significant number of patients — Ferrer pegged the number at 60% — are not hospitalized specifically for COVID-19 but have tested positive after seeking treatment for other reasons. But each presents a particular strain on resources because of the additional services needed to keep them from spreading the virus.
Hospitalizations are also a lagging indicator of coronavirus spread; as long as coronavirus transmission remains elevated, patient counts are unlikely to tail off significantly. And even as transmission peters out, it can take weeks for that trend to provide relief.
Also yet to be seen are the impacts of the BA.4 and BA.5 subvariants, which are growing increasingly dominant nationwide.
Even though hospitals are not reporting being overwhelmed now, Ferrer said the plan to reinstate a mask mandate should hospitalizations worsen is prudent.
“Waiting until hospitals are overwhelmed is way too late to try to do much about slowing transmission,” Ferrer said. “The time to slow transmission is actually when you start seeing indicators that you’re having more utilization at your hospitals.”
The CDC recommends that everyone age 2 and older wear masks in indoor settings when a county reaches the high COVID-19 community level, which includes both hospitalization and coronavirus case rates.
When those indicators are high, “that’s the time to start getting worried and to start trying to do something to slow down transmission,” Ferrer said.
“We’re not going to be able to completely eliminate transmission of these highly infectious new subvariants, but we can definitely make a better effort to slow transmission down so that the increases at the hospitals don’t end up creating the kind of stress that we saw both during the Omicron winter surge and the previous winter surge,” Ferrer said.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.