How big a threat is the Omicron variant of coronavirus? Here’s what we know
- Share via
The recent discovery of the Omicron variant of the coronavirus has upended the outlook for a pandemic that already was expected to get worse over the winter.
But it will probably take weeks before scientists truly understand whether Omicron — declared a “variant of concern” by the World Health Organization on Friday, two days after South Africa announced its detection — will end up being as significant as the Delta variant.
“It will take approximately two more weeks to have more definitive information on the transmissibility, severity and other characteristics of the variant,” the White House said in a statement Sunday after President Biden met with his COVID-19 response team.
The statement said that Dr. Anthony Fauci, Biden’s chief medical advisor for the pandemic, “continues to believe that existing vaccines are likely to provide a degree of protection against severe cases of COVID.” Fauci also reiterated that booster shots for fully vaccinated individuals provide the strongest available protection from COVID.
Not all variants of concern end up becoming a big deal.
Two — Beta, first identified in South Africa, and Gamma, first identified in Brazil — never became as consequential globally as Delta has become.
How you can protect yourself amid Omicron variant alarms: Here’s what we know.
Still, there are many reasons why officials are expressing deep concern about Omicron even as they acknowledge there is still a lot unknown and it’s possible this variant may peter out.
The Omicron variant has not yet been detected in California or the U.S., although experts say they fully expect it. Confirmed cases already have been reported in the Canadian province of Ontario.
Here’s what we know, as well as questions that remain unanswered:
Is Omicron more transmissible than other variants?
Fauci said Sunday on ABC’s “This Week” that Omicron is probably more transmissible than other variants.
Its mutations “would strongly suggest that it would be more transmissible,” Fauci said. Troublingly, “it might evade some of the protection of monoclonal antibodies,” a treatment for COVID-19 that can counteract the coronavirus before it can begin destroying the body’s organs.
“If you look at the pattern of what’s going on right now in southern Africa — particularly in South Africa — when you have a spike of infections, they are very heavily weighted toward this new variant, the Omicron,” Fauci said. “And, therefore, you have to presume that it has a good degree of transmissibility advantage.”
In another interview Sunday on NBC’s “Meet the Press,” Fauci said Omicron’s sudden appearance in South Africa was accompanied by a big spike in cases, following a time of low infection levels.
“And when the South Africans looked at it, they said, ‘Oh, my goodness. This is a different virus than we’ve been dealing with.’ So it clearly is giving indication that it has the capability of transmitting rapidly,” Fauci said. “That’s the thing that’s causing us now to be concerned, but also to put the pressure on ourselves now to do something about our preparation for this.”
It’s not clear whether Omicron will overtake Delta as being the most transmissible variant of the coronavirus.
While Omicron is highly contagious, “what we don’t know is whether it can compete with Delta,” Dr. Francis Collins, director of the National Institutes of Health, said in an interview with CNN’s “State of the Union” program Sunday.
Officials were worried many months ago about the Beta variant, but in the U.S., Beta “never really took off because Delta was so incredibly effective at spreading that it couldn’t compete,” Collins said.
L.A. County health officials are urging the public to wear masks in indoor public settings and at outdoor “mega events” and be vaccinated.
Are the current vaccines less robust against Omicron?
It’ll probably take two weeks to know whether the vaccines would be less effective against the Omicron variant. Lab tests are underway.
Will vaccinations and boosters protect people?
Past experience with other well-studied variants, including Delta, shows that vaccinations and boosters still generate enough antibodies to provide protection against the coronavirus.
“I don’t think there’s any possibility that this [Omicron variant] could completely evade any protection by a vaccine. It may diminish it a bit, but that’s the reason why you boost,” Fauci said on ABC.
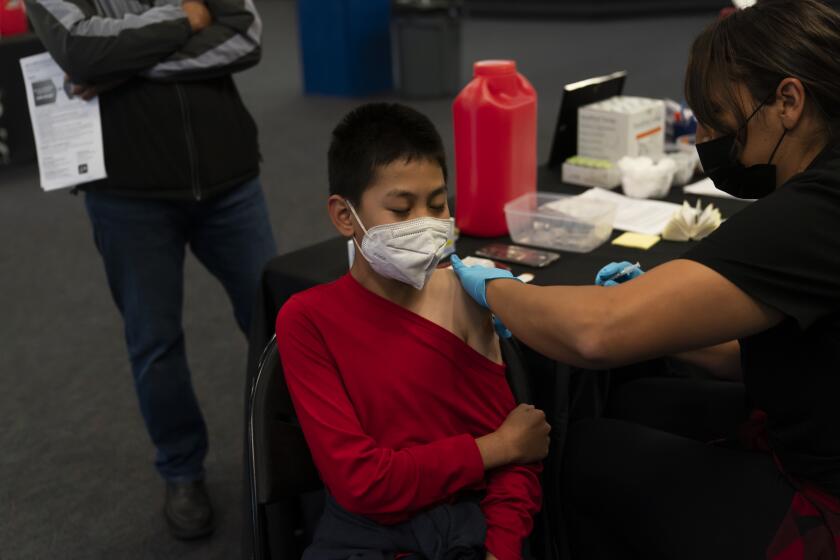
That’s also why it’s important that anyone who is unvaccinated — including children 5 and older — get their shots, and fully vaccinated adults get boosters, Fauci said.
Fauci said on NBC that vaccinated people should not wait to get boosters, thinking a more up-to-date vaccine will be coming shortly.
“Get boosted now,” he said.
“When you get boosted, the level of your antibody goes way, way above what the level at its peak was after the second dose. So the booster not only gets you back up to where you were, it gets you way, way, way up,” Fauci said.
The worst-case scenario is that the vaccines now available don’t provide any protection against Omicron, but that is unlikely, experts say.
Dr. Ashish Jha, dean of Brown University’s School of Public Health, said there is no way Omicron will globally revert to the state of the pandemic that emerged nearly two years ago.
“Our vaccines MAY take a hit but will still provide some (may be a lot) protection,” Jha tweeted. “We are in a MUCH better place. This isn’t March 2020.”
A return to border and social restrictions could upend months of progress in countries such as Singapore, often a bellwether for the rest of Asia.
Will vaccines need to be updated for Omicron?
Pfizer and Moderna are working on potential new vaccines designed specifically against Omicron, but it’s not clear they will be needed, Collins said in an interview with the news program “Fox News Sunday.”
“All of us hope we don’t need to do that,” he said.
What do the experts think?
Dr. Scott Gottlieb, a former commissioner with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration and a member of Pfizer’s board, said Sunday on CBS’ “Face the Nation” that many experts are confident that vaccinated people who have gotten booster shots will be protected.
“That third dose of the vaccine provides a much broader level of immunity. So it’s not just more antibodies that you develop, but you develop antibodies against more parts of the virus,” Gottlieb said.
A number of vaccine experts “feel reasonably confident that three doses of vaccine is going to be protective.”
Gottlieb said there could be a situation in which lab tests show that blood plasma from those with protection from COVID-19 and exposed to the Omicron variant may suggest that “the neutralization against this virus decline substantially” — which, at first glance, would seem discouraging. This was a big concern with the Beta variant.
But in real-world conditions, the Pfizer and Moderna vaccinations ended up being almost equally effective against the Beta variant as the initial strain of the coronavirus, Gottlieb said. “You could see a decline in neutralization, and the vaccines will still be effective.”
Here’s more information on the variant, and a look at the current state of California’s handling of COVID-19.
Does Omicron produce more severe illness?
There have been reports that those infected in South Africa have had mild illnesses. But that may be the result of the initial group being “mostly young people, who have mild illness anyway. So, I would say we just don’t know,” Collins told CNN.
The initial reported infections have occurred among university students.
The World Health Organization said that “preliminary data suggests that there are increasing rates of hospitalization in South Africa, but this may be due to increasing overall numbers of people becoming infected, rather than a result of specific infection with Omicron. There is currently no information to suggest that symptoms associated with Omicron are different from those from other variants.”
Could differences in vaccination rates affect Omicron’s spread?
South Africa has a relatively low vaccination rate. According to Our World in Data, about 24% of the population is fully vaccinated; in the U.S., about 58% are fully vaccinated.
Five nations in southern Africa — South Africa, Zimbabwe, Namibia, Mozambique and Malawi — have told Pfizer to “slow down or stop shipping vaccines because they haven’t been able to distribute what they’ve received,” Gottlieb said.
South Africa has also told J&J and Pfizer to throttle back or stop shipments because they have an excess of vaccine, Gottlieb said. Of 30 million Pfizer doses sent to South Africa, only 19 million have been used, he said.
Many health experts believe mask mandates and tougher vaccine requirements will be needed in the coming months to avoid more serious coronavirus surges.
What about the Delta variant?
The attention on Omicron might obscure the fact that the Delta variant continues to be a significant threat to California and the U.S.
“While attention has turned to Omicron, its functional impact yet unknown, the main issue is that Delta is rampant in many countries in Europe and the United States,” tweeted Dr. Eric Topol, director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute in La Jolla.
The Delta variant comprises virtually all of the analyzed coronavirus cases in the U.S., according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
As of Tuesday, new daily COVID-19 hospitalizations nationwide were up by 20% compared with the first week of November.
California saw a troubling uptick in hospitalizations in late October, though numbers have declined in November. Still, health officials in areas with low vaccination rates, such as the San Joaquin Valley, say that hospitals continue to be full and have sought help in transferring some patients to places like L.A. County.
And computer models published on the state’s California COVID Assessment Tool website show some scenarios suggesting a surge in hospitalizations is possible by late winter, particularly if too few vaccinated adults get a booster shot.
It’ll take a couple of weeks before officials in California know whether a surge linked to gatherings over Thanksgiving occurs.
“Already, we’re seeing in different states throughout the United States that — especially in the Midwest and the East, where people are going indoors because of weather changes — we’re seeing high levels of cases,” Dr. Regina Chinsio-Kwong, a deputy health officer for Orange County, said Wednesday.
“And there are some areas still in California that still have high case rates. So I’m hoping that we can stave off another surge until 2022. But there’s still a potential to see a little bit of an increase in December,” Chinsio-Kwong said.
The Omicron variant, first identified in South Africa, has more mutations than any scientists have seen, including some that may make it less susceptible to immunity generated from previous infections or vaccines.
How can people protect themselves?
Besides getting vaccinated or boosted, the California Department of Public Health also “recommends everyone wear masks in indoor public places (such as grocery stores and movie theaters) regardless of vaccination status,” the agency said in a statement.
Indoor mask mandates in public areas are required in a number of counties in California, including Los Angeles and Ventura counties, as well as much of the San Francisco Bay Area.
In addition, the California Department of Public Health said, “you should immediately get tested for COVID-19 if you are feeling any symptoms — regardless of your vaccination status. COVID-19 symptoms can feel like a common cold (including just ‘the sniffles’), seasonal allergies or flu. COVID-19 testing in California is free to anyone who needs it.”
People should also test themselves three to five days after travel “to help us stay vigilant for new cases and variants,” California state epidemiologist Dr. Erica Pan said in a tweet.
More to Read
Sign up for Essential California
The most important California stories and recommendations in your inbox every morning.
You may occasionally receive promotional content from the Los Angeles Times.